| pA2
online © Copyright 2003 The British Pharmacological Society |
010P
University of Surrey Summer Meeting June 2003 |
The
effect of a non-peptide CGRP antagonist, BIBN4096BS, in murine cutaneous
microvasculature
|
Print abstract Search PubMed for: |
Calcitonin gene-related peptide
(CGRP) is one of the most potent microvascular vasodilators (Brain et al., 1985). CGRP has been implicated in the onset of migraine, stimulating
the search for a non-peptide CGRP antagonist. BIBN4096BS has been shown
to be a potent antagonist in vitro and in vivo with 200
fold increased selectivity for human and marmoset receptors compared with
rat (Doods et al., 2000). Microvascular vasodilators potentiate
the oedema formation caused by mediators of increased microvascular permeability
in species including the mouse (Cao et al., 1999). The aim of this
study was to investigate the ability of BIBN4096BS to modulate the ability
of vasodilators, vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP), CGRP, adrenomedullin
(ADM) and prostaglandin E1 (PGE1),
to potentiate plasma extravasation induced by substance P (SP) in mouse
skin.
Female CD1 mice (20-25g) were anaesthetised with urethane (2.5mg/g, i.p.)
and 3.6kBq 125I-BSA injected i.v. Plasma
extravasation was assessed as the extravascular accumulation of 125I-BSA.
VIP (3pmol/site), CGRP (1pmol/site), ADM (300pmol/site) or PGE1
(300pmol/site) were administered intradermally in the presence or absence
of SP (300pmol/site). BIBN4096BS was co-injected intradermally (300pmol/site)
where necessary. After thirty minutes, blood samples were taken by cardiac
puncture, and plasma and skin sites assessed for radioactivity. Plasma
extravasation was expressed as µl of plasma per gram of tissue.
Results are shown as mean ± s.e.mean and statistical analysis was
by ANOVA and Bonferroni's modified t test.
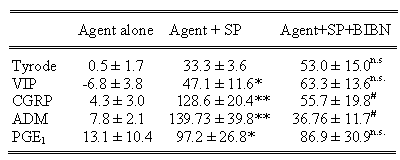
When administered alone, the vasodilators induced no plasma extravasation,
as expected. However, all agents significantly potentiated the plasma
extravasation to SP (see Table 1). BIBN4096BS only inhibited the effect
of CGRP and ADM in potentiating SP. The results indicate that BIBN4096BS
selectively blocks CGRP and ADM responses, implying that both CGRP and
ADM act via the CRLR/RAMP1 (CGRP) receptor complex in the murine microvasculature.
Table 1. Effect of BIBN4096BS (BIBN) on the potentiation of SP-induced
plasma extravasation by vasodilators. *=p<0.05, **=p<0.01 compared
to SP alone, #=p<0.05, compared to agent + SP (n=4-11).
Brain, S.D. et al.,
(1985). Nature, 313, 54-6.
Cao, T. et al., (1999). Am. J. Physiol, 277, 476-481.
Doods, H. et al., (2000). Br. J. Pharmacol., 129,
420-3.
C. T. is funded by the British Heart Foundation.