| pA2
online © Copyright 2003 The British Pharmacological Society |
027P
University of Surrey Summer Meeting June 2003 |
Localisation
of apelin-12, a ligand for the orphan G-protein coupled with APJ receptor,
to human cardiovascular tissue
|
Print abstract Search PubMed for: |
Apelin, a 36
amino acid peptide recently isolated from bovine stomach, is the endogenous
ligand of the orphan G-protein coupled receptor APJ (Tatemoto et al.,
1998). We have pre-viously demonstrated the presence of high affinity
[125I]apelin-13 binding sites in human
heart, aorta, coronary artery and sa-phenous vein and identified p[Glu]
apelin-13 as a potent vaso-constrictor of human saphenous vein (Katugampola
et al., 2001). Our aim was to determine the distribution of apelin-12-like
immunoreactivity in human tissues using an antibody raised against the
C-terminal dodecapeptide of apelin.
For immunocytochemistry, human tissues were obtained with ethical approval.
Left ventricle and atria were from patients transplanted for ischaemic
heart disease (n=8), cardiomyopathies (n=6), cystic fibrosis (n=3), or
from donor hearts for which there was no suitable recipient (n=3). Sections
of histologically normal kidney (n=5) and lung (n=5) were from patients
undergoing nephrectomy and lobectomy respectively for non-obstructive
carcinomas. Adrenal was from one patient undergoing adrenalectomy for
phaeochromocytoma.Cryostat sections (10µm) of tissues were fixed
in ice-cold acetone for 10 min. Sections were blocked with 5% swine serum
in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) for 1h at 23°C and incubated with
an anti-apelin-12 polyclonal antibody (Phoenix Pharmaceuticals, CA. USA)
at a dilution of 1:500, at 4°C for 72h, in PBS containing 0.01% tween-20
and 1% swine serum. Specific staining was detected using the peroxidase
anti-peroxidase method. Adjacent sections were incubated with non-immune
serum as a negative control.
Fig. 1 Apelin-LI localised to human intramyocardial (A) and adrenal plexus
(B) arteries. Scale bar = 200µm.
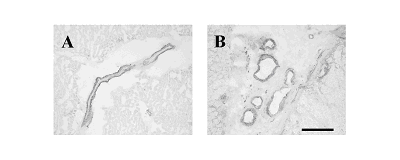
Intense apelin-12-like
immunoreactivity (apelin-LI) was localised to the endothelium of intramyocardial
(Fig. 1), intrarenal and small pulmonary blood vessels and to endocardial
endothelial cells lining the atria. Little or no staining was observed
in smooth muscle, cardiomyocytes or epithelial cells in lung or kidney.
In adrenal gland, apelin-LI was confined to endothelial cells of surrounding
arteries, small resistance arteries within the capsular plexus (Fig. 1)
and the central vein. Staining was not detected in secretory cells of
the adrenal medulla and cortex.The presence of apelin-LI in vascular endothelial
cells sug-gests that in the human cardiovascular system apelin may act
as a vasoactive mediator that elicits its function by activation of receptors
present on the underlying vascular smooth muscle and myocardium.
MK supported by Isaac Newton and Cambridge European Trusts.
Katugampola, S.D., Maguire, J.J., Matthewson, S.R. & Davenport, A.P.
(2001). Br. J. Pharmacol., 132, 1255-1260.
Tatemoto, K., Hosoya, M., Habata, Y., et al., (1998). Biochem.
Biophys. Res. Commun. 251, 471-476.