| pA2
online © Copyright 2003 The British Pharmacological Society |
041P
University of Surrey Summer Meeting June 2003 |
|
The effect of chromanol 293B in isolated and perfussed guinea pigs hearts
M. Maginn, O. Åkerlund and J. Matz. Department of Safety Pharmacology. H. Lundbeck A/S. Copenhagen. Denmark. |
Print abstract Search PubMed for: |
Torsade de Pointes
(TdP) is a rare form of polymorphic ventricular tachycardia (VT) which
is preceded by a delay of ventricular repolarisation. Drug induced delay
of ventricular repolarisation has been considered to be due to IKr
blockade. However the other major potassium channel responsible for repolarisation,
IKs, has been considered less of a concern (Ding et al.,
2002). The chromanol derivative 293B was found to be a potent blocker
of the IKs current in guinea pig ventricular myocytes (Busch
et al., 1996). The aim of this study was to examine the role of
IKs blockade and its anti-arrhythmic potential in the isolated
and perfused guinea pig heart model.
Male guinea pigs were anaesthetised with sodium pentobarbital (250 mg/kg,
i.p.) and the hearts were removed and perfused via the aorta with Krebs-Heinselett
solution. The hearts were paced at 273 ms CL. A water filled balloon connected
to a force transducer was inserted into the left ventricle via the left
atria to measure the maximum left ventricular prerssure (LVPmax). Following
an equilibration period the hearts were infused with either vehicle (0.5%
DMSO) or chromanol 293B (1.0, 10.0 or 30 µM) for 40 min. The electrocardiograms
and ventricular waveforms were digitised and the QT interval and LVPmax
were measured. Drug treatments were compared to the time matched vehicle
group at 273 ms. All data are presented as mean ± S.E.M.
There were no significant difference between the QT pre-dose values (p>0.05,
Student t-test). Chromanol 293B (30 µM) significantly increased
QT interval compared to vehicle (p<0.05, Student t-test).See Table
1.
Table 1: Effect of Chromanol 293B on the QT interval (ms) and LVPmax (mmHg)
at pre-dose and 40 min infusion.
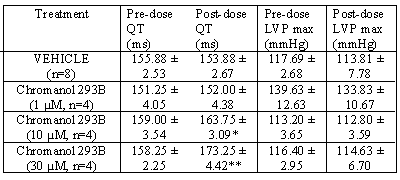
*p<0.05 &
**p<0.01 (Student t-test, vs time matched vehicle group).
In conclusion, the blockade of the slow component delayed rectifier K+
current (IKs) by chromanol 293B induces a moderate prolongation
in the QT-interval at high concentrations (10 & 30 µM). This
is approximately 5-fold higher than the IC50
for the IKs channel by chromanol 293B in guinea pig ventricular
myocytes (Busch et al., 1996). In addition the LVPmax was not affected
and this agrees with findings that chromanol 293B has no effect on the
cardiac sodium or L-type calcium channels (Bosch et al., 1998).
Drug induced IKs blockade may in it self induce repolarisation
delays as noted in this in vitro Langendorff heart model.
Bosch RF, et al., (1998) Cardiovasc. Res. 38,
441-450.
Busch AE, Siessbrich, H. et al., (1996) Pflugers. 432,
1094-1096.
Ding, WG, Toyoda, F and Matsuura, H. (2002) Br. J. Pharmacol. 137,
253-262.