| pA2
online © Copyright 2003 The British Pharmacological Society |
042P
University of Surrey Summer Meeting June 2003 |
|
Ifenprodil effects on pulmonary function in unrestarined rats a whole body plethysmograph study M. Maginn, S. Albrechtsen, and J. Matz. Department of Safety Pharmacology, H. Lundbeck A/S. Copenhagen. DK 2500. |
Print abstract Search PubMed for: |
Ifenprodil (IFEN)
is marketed as Vadilex®, a competitive inhibitor of noradrenaline
for the treatment of transient ischaemic attack and generalised symptoms
of mental deterioration. Studies have shown however that IFEN acts as
an NMDA2B, L-type Ca 2+
and ![]() 1
antagonist (Boyce et al., 1999). The clinical signs observed following
dosing with IFEN have included ptosis and acute respiratory distress.
The aim of this study was to qualitatively measure the effects of IFEN
on pulmonary function in unrestrained rats, using a single chamber plethymograph
(EMKA, Paris, France). The inspiratory and expiratory flows are indirectly
measured based on pressure differences due to the addition of heat and
moisture in the expired air (DeLorne and Moss, 2002).Male Wistar rats
(180-200 g; Møllegård & Bomholdtgård A/S Denmark)
were randomised into three groups to receive either IFEN (2 or 20 mg/kg),
or saline vehicle (dose volume 5 ml/kg). The rats were placed in the chamber
for 2 hours prior to dosing and were returned to the chamber following
intraperitoneal dosing for an additional 2 hr post recording.
1
antagonist (Boyce et al., 1999). The clinical signs observed following
dosing with IFEN have included ptosis and acute respiratory distress.
The aim of this study was to qualitatively measure the effects of IFEN
on pulmonary function in unrestrained rats, using a single chamber plethymograph
(EMKA, Paris, France). The inspiratory and expiratory flows are indirectly
measured based on pressure differences due to the addition of heat and
moisture in the expired air (DeLorne and Moss, 2002).Male Wistar rats
(180-200 g; Møllegård & Bomholdtgård A/S Denmark)
were randomised into three groups to receive either IFEN (2 or 20 mg/kg),
or saline vehicle (dose volume 5 ml/kg). The rats were placed in the chamber
for 2 hours prior to dosing and were returned to the chamber following
intraperitoneal dosing for an additional 2 hr post recording.
The waveforms were stored and measured digitally as a mean of 100 waveforms
at each time point using the IOX v1593 software (EMKA, Paris, France).
The results are expressed as a mean ± S.E.M. (n=8). IFEN significantly
(p<0.05) increased the peak inspiratory flow (PIF (ml/min)), peak expiratory
flow (PEF (ml/min)), minute volume (MV (ml/min2)),
inspiration tidal volume (TV (ml)), expired volume (EV (ml)), relaxation
time (RT (ms)), expiratory time (Te (ms)) and the lung resistance parameter
PENH (PENH=(PEF/PIF)((Te/RT)-1)) compared to the time matched vehicle
control group. The results are shown on Table 1.
Table 1: Effect of IFEN on pulmonary function in the rat.
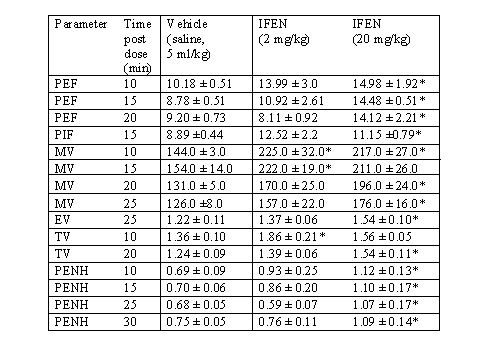
*p<0.05 vs
time matched vehicle group (Student t-test).
In conclusion IFEN dose dependently and significantly increases the rate
and volume of respiration. This may be due to antagonism of the NMDA receptors
in the ventral medullary respiratory neuronal group in the rat.
Boyce S, et al., (1999) Neuropharmacology, 38(5):611-623.
Delorne MP. & Moss OR. (2002) J.Pharm & Toxicol. Methods,
47, 1-10.