| pA2
online © Copyright 2003 The British Pharmacological Society |
058P
University of Surrey Summer Meeting June 2003 |
|
Characterisation of [3H]-ZM 241385 binding in wildtype and A2A knockout mouse brain
M.D.W. Kelly,
*C. Ledent, I. Kitchen & S.M.O. Hourani, School of Biomedical
and Life Sciences, University of Surrey, Guildford, Surrey, UK.
*IRIBHN, Université Libre de Bruxelles, Bruxelles, Belgium. |
Print abstract Search PubMed for: |
[3H]-ZM
241385 has been shown to be a highly selective, high affinity adenosine
A2A receptor antagonist ligand in the
rat brain (Alexander et al., 2001). Adenosine A2A
receptor knockout mice have been generated (Ledent et al., 1997),
and provide a unique opportunity to explore the true selectivity of this
ligand. In this study we have therefore used [3H]-ZM
241385 to quantify and localise the distribution of adenosine A2A
receptors in the brain and spinal cord of both wild-type (+/+) and A2A
knockout (-/-) mice.
Adult male +/+ CD1 mice (30-35g) and their -/- littermates were obtained
from an in-house breeding programme, killed by cervical dislocation and
their brains and spinal cords removed. Saturation binding was carried
out in triplicate in homogenates of brain (minus cerebellum) for 30 min
as described by Alexander et al. (2001). The concentration range of [3H]-ZM
241385 used was 0.25-16nM and non-specific binding was determined in the
presence of 5mM theophylline. Saturation analysis was carried out using
Graph Pad PRISM. Autoradiographic binding and quantitative analysis were
carried out as previously described (Kitchen et al., 1997). Both
coronal and sagittal sections (20 µm) cut at 300µm intervals
throughout the brain were exposed to 2.5nM [3H]-ZM
241385 for 90 min and non-specific binding was determined using 5mM theophylline
(Alexander et al., 2001).
Saturable specific binding was observed in the homogenate binding studies
in tissues from +/+ mice, with a Bmax
of 299.1 ± 28.4 fmolmg-1 protein
and a KD of 0.75 ± 0.08nM (n=5).
Specific binding at KD was 90-95%. Only
a low level of non-saturable binding, 5.0 ± 1.2 fmolmg-1
protein at KD (n=4), was observed in
-/- brain homogenates (Figure 1).
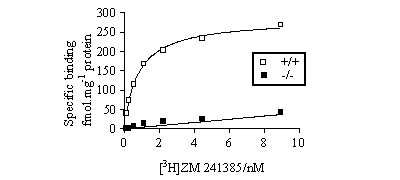
Figure 1. Specific
binding of [3H]-ZM 241385 to brain homogenates
from +/+ and -/- mice. Similar results were found in each of at least
4 experiments.
Specific binding of [3H]-ZM 241385 (fmol/mg,
n=5, mean ± s.e.m) in +/+ brain slices was confined to the caudate
putamen (525.7 ± 69.9), nucleus accumbens (core 369.9 ±
61.2, shell 260.8 ± 25.3), olfactory tubercle (955.1 ± 87.4)
and globus pallidus (169.5 ± 44.4). In all other regions of the
brain and spinal cord specific binding was either below the limits of
detection or <3.0 fmolmg-1, as was
binding in -/- brains.
Overall these results confirm the selectivity of [3H]-ZM
241385 as a radioligand for A2A receptors,
and also confirm the lack of A2A receptors
in the spinal cord and extrastriatal brain regions of the mouse, as previously
shown using the agonist radioligand [3H]
CGS 21680 (Bailey et al., 2002).
Alexander S.P. et al. (2001). Eur. J. Pharm. 411,
205-210.
Bailey A. et al. (2002). Brain Res. 943, 68-79.
Kitchen I. et al. (1997). Brain Res. 778, 73-78.
Ledent C. et al. (1997) Nature 388, 674-678.