| pA2
online © Copyright 2003 The British Pharmacological Society |
064P
University of Surrey Summer Meeting June 2003 |
|
The effects of chronic administartion of fluoxetine on 8-OH-DPAT-induced hypophagia in fasted rats
Richard
M. Tite, Melanie Down, Sabrina Jhugroo & Ivor S. Ebenezer. Neuropharmacology
Research Group, School of Pharmacy and Biomedical Sciences, University
of Portsmouth, Portsmouth, PO1 2DT, U.K. |
Print abstract Search PubMed for: |
It has been previously
demonstrated that 5HT1A receptor agonist, such as 8-OH-DPAT and ipsapirone,
inhibit food intake in fasted rats by an action at central 5-HT1A
receptors (Ebenezer, 1992; Arkle et al., 2001). It is also been
reported that chronic administration of serotonin reuptake inhibitors
(SSRIs), such as fluoxetine, desensitise both pre- and postsynaptic 5HT1A
receptors (see Pejchal et al., 2002). The present study was undertaken
to investigate whether chronic administration of fluoxetine would affect
the hypophagic effects of 8-OH-DPAT in fasted rats.
Male Wistar rats (b.wt. 300 - 340g; n=16) were randomly divided into 2
equal groups. Rats in Group 1 (Control Group) were injected i.p. once
daily with physiological saline solution for 28 days, while rats in Group
2 (Treatment Group) were injected i.p. once daily with fluoxetine (10
mg kg-1). Following treatment, the animals
in both groups were fasted for 22h and injected s.c. with either saline
or 8-OH-DPAT (100 µg kg-1). Immediately
after injection, the animals were placed singly in experimental cages
and food intake measured over a 2h period. Each rat received both treatments
in a random fashion.
The results are illustrated in Fig.1. The rats treated chronically with
fluoxetine lost approximately 15% of their body weight over the 28 day
treatment period compared with the animals chronically treated with saline
(data not shown). 8-OH-DPAT significantly inhibited cumulative food intake
in the rats chronically treated with saline (Control Group) at each of
the measurement intervals over the 2h period (Fig. 1A). By contrast, 8-OH-DPAT
did not significantly affect feeding at any of the measurement intervals
in the rats chronically treated with fluoxetine (Treatment Group; Fig.
1B).
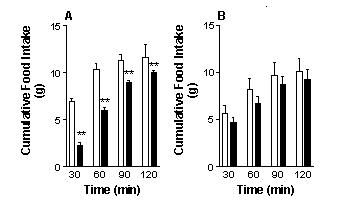
Fig. 1. The effects
of 8-OH-DPAT (100 µg kg-1; s.c.)
on cumulative food intake in rats that had been (A) chronically treated
with saline (Control Group) or (B) fluoxetine (Treatment Group). ![]() Saline
Saline ![]() 8-OH-DPAT.Vertical
line rep. s.e. mean. **P<0.01 (paired t-test).
8-OH-DPAT.Vertical
line rep. s.e. mean. **P<0.01 (paired t-test).
The results show that chronic administration with the SSRI anti-depressant
drug fluoxetine abolishes the suppressant effects of 8-OH-DPAT on food
intake in food-deprived rats. Similar results have been obtained with
the tricyclic antidepressant drug des-imipramine. These finding provide
behavioural support for the notion that chronic administration with antidepressant
drugs desensitise central 5-HT1A receptors.
Furthermore, it is possible that the method described here may prove to
be useful as a novel in vivo test to assess psychoactive compounds
for antidepressant activity.
Ebenezer, I.S. (1992) NeuroReport 3, 1019-1022.
Arkle, M. et al. (2000) Eur. J. Pharmacol., 408,
273-276.
Pejchal, T. et al. (2002) Br. J. Pharmacol., 135,
1115-1122.