| pA2
online © Copyright 2003 The British Pharmacological Society |
065P
University of Surrey Summer Meeting June 2003 |
|
Ifenprodil induced disruption in rat rotarod performance is potentiated by verapamil
|
Print abstract Search PubMed for: |
Ifenprodil
(IFEN) is marketed as Vadilex®, for the treatment of transient ischaemic
attack and generalised symptoms of mental deterioration related to cerebrovascular
insufficiency (Boyce et al. 1999). It was further shown however
that IFEN acts as an NMDA2B, L-type Ca
2+ and œ1
adrenoceptor antagonist (Boyce et al., 1999). Previous studies
have examined the effects of IFEN and more selective NMDA2B
antagonists in rotarod performance in rats (Boyce et al., 1999).
The results suggested that IFEN decreased rotarod performance, which is
not noted with more selective NMDA2B antagonists. The aim of this study
was to examine L-type Ca+ involvement
in the IFEN effect on rotarod performance, by co-administering IFEN with
verapamil (VER) in rats and testing rotarod performance.
To determine the effects of IFEN and verapamil on motor co-ordination,
male Wistar rats (180-200 g; Møllegård & Bomholdtgård
A/S., Denmark) were first trained on the rotarod on four separate occasions,
2 times per day starting two days before the test. The animals were trained
to remain for 120 s on a Harvard Apparatus Coordin8® accelerating
rotarod (increasing from 4 to 12 r.p.m.). Any animal that fell off the
wheel within the first 30 s was replaced on the wheel and retested. On
the day of testing the animals were then randomised into separate groups
to receive either IFEN (2, 10 or 20 mg/kg) or saline vehicle (dose volume
5 ml/kg). IFEN was administered intraperitoneally 60 min prior to testing
and VER 2.0 and 20 mg/kg or saline (dose volume 5 ml/kg) was administered
intraperitoneally 30 min prior to testing. The animals were placed on
the accelerating rotarod (increasing from 4 to 40 r.p.m. during a 5 min
period) and the time for which the rats were able to remain on the rotarod
was recorded. The results are expressed as time (sec) on the wheel.
Table 1: Effect of IFEN and verapamil on rotarod performance
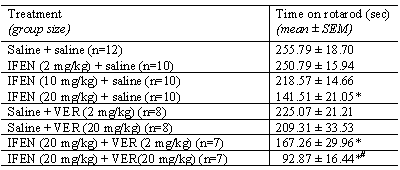
*p<0.01
IFEN (20 mg/kg) vs vehicle, *p<0.05 IFEN (20 mg/kg) + VER (20 mg/kg)
vs IFEN (20 mg/kg), #p<0.01 VER (20 mg/kg) + IFEN (20 mg/kg) vs IFEN
20 mg/kg + VER (2 mg/kg) (Repeated measures ANOVA followed by a Dunnett's
Multiple Comparison test when p< 0.05).
IFEN behavioural effects are in contrast to the lack of effects of more
selective NMDA2B antagonists (Gill et al., 2002; Higgins et al., 2003). Although verapamil alone
had no effect, in combination with IFEN it significantly reduced rotarod
performance. Out data suggest that L-type Ca2+
channel blockade may be involved in the behavioural effects of IFEN.
Boyce S, et al., (1999) Neuropharmacology, 38, 611-623.
Higgins GA, et al., (2003) Neuropharmacology, 44,
324-341.
Gill R, et al., (2002) J. Pharm & Exp. Ther., 302,
940-948.