| pA2
online © Copyright 2003 The British Pharmacological Society |
067P
University of Surrey Summer Meeting June 2003 |
|
The role of a binding loop of residue in the function of the mouse 5-HT3A receptor
|
Print abstract Search PubMed for: |
The 5-HT3
receptor (5-HT3R) is
a homo-pentameric member of the Cys-loop family of ligand-gated ion channels
in which 6 binding loops (A-F) compose the binding site. The extracellular
domain of 5-HT3R has a similar
structure to the recently crystallized Lymnaea acetylcholine binding
protein (AChBP). A computer-generated model of the 5-HT3
receptor structure based on the AChBP structure only places one residue
from binding loop A (N128) within 5 Å of the docked 5-HT. In the
preferred model of the 5-HT molecule in the binding site, the keto group
of residue N128 potentially forms hydrogen bonds with the hydroxyl group
of 5-HT (Reeves et al., 2003). To test the accuracy of the model,
we therefore analyzed the role of residue N128 in the binding and function
of the 5-HT3 receptor by replacing
it with a range of different amino acids.
N128 was mutated using the Kunkel method (Kunkel, 1985) in the expression
vector pcDNA3 (Invitrogen), transfected into HEK 293 cells using calcium
phosphate precipitation (Chen and Okayama, 1988) and stable cell lines
were selected using geneticin (Life Technologies). Colonies with the highest
expression of the 5-HT3R were selected
based on 2-point radioligand binding affinity Radioligand binding activity
was characterized with the antagonist [3H]-granisetron
(Spier et al., 2000) and receptor function in response to 5-HT
was analysed using fluorescent imaging of changes in membrane potential
(Baxter et al., 2002; Hargreaves et al., 1994).
Table I [3H]-granisetron Kd values and 5-HT pEC50 values
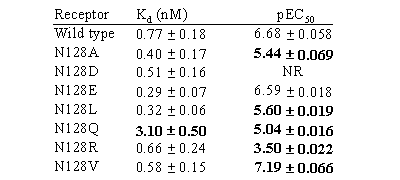
Values are mean
± s.e.mean for normalized data, n=4-11. Bold font indicates mutants
that are significantly different from wild type (P<0.01, ANOVA). NR
= no response up to 300µM.
Binding affinities for all mutants were similar to wild-type suggesting
that N128 does not play a critical role in granisetron binding. Since
E and V could substitute effectively for N in 5-HT-induced responses,
but A, Q, R, and D resulted in an increased EC50
or loss of function, neither the size nor the charge of this residue is
critical. It is also unlikely that N128 forms a hydrogen bond with 5-HT
because V is an effective substitute for N. These results suggest that
N128 has an important but complex role in receptor function.
Baxter D.F. et al. (2002) J. Biomol. Screen. 7, 79-85.
Chen, D. et al. (1988) Biotechniques 6, 632-8.
Hargreaves, A.C. et al. (1994) Mol. Pharmacol. 46,
1120-1128.
Kunkel, T.A. (1985) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82, 488-492.
Reeves, D. et al. (2003) Biophys. J. 84: 2338-2344.
Spier, A.D. et al. (2000) J. Biol. Chem. 275, 2650-2655.