| pA2
online © Copyright 2003 The British Pharmacological Society |
047P
University
of Manchester Autumn Meeting September 2003 |
|
The role
of the zona incerta in a genetic rat model
|
Print Abstract Search PubMed
for: |
Absence epilepsy can be described as a paroxysmal loss of consciousness of abrupt onset and termination associated with a bilateral synchronous spike and wave discharge (SWD), which can be recorded on the electroencephalogram (EEG). These seizures are known to involve an interaction between thalamic and cortical structures, more specifically the reticular thalamic nuclei (nRT), thalamic neurons (TC) (Danober et al., 1998) and the peri-oral region of the somatosensory cortex (S1po) (Meeren et al., 2002). However, recent evidence has suggested that the zona incerta (ZI) may also be involved in sustaining seizure activity, due to its direct GABAergic projections to the thalamus (Barthó et al., 2002). In this investigation, we bilaterally microinfused either ethosuximide (ETX), a first line anti-absence drug, classically believed to act by reducing IT (low voltage Ca2+ current) (Coulter et al., 1989) or CGP 36742, a GABAB antagonist, into the ZI and measured the effects on SWD.
Male Genetic Absence Epilepsy Rats from Strasbourg (GAERS) (323g±5g) were anaesthetised with ketamine/medetomidine (75 & 0.5 mg/kg i.p. respectively) and implanted with a twisted bipolar EEG electrode into the frontal cortex at an angle of 20° to the vertical, in an anterior direction (mm relative to Bregma: AP; +3.2, L; +2.4, V; +2.8) and, bilaterally with guide infusion cannulae into the ZI (AP; -4.3, L; ±2.4, V; +6.3). The following day, the EEG signal was amplified, filtered and recorded (BioAmp ML-136, PowerLab 2/20, ADInstruments) for a 30 min basal period. Either ETX (20 or 200nmol/side), CGP 36742 (5nmol/side) or 0.9% saline was then microinfused, at a flow rate of 0.5µl/min for 2 min. EEG continued to be recorded for a subsequent 2 x 30 min periods. SWD are expressed as the percentage of each 30 min period.
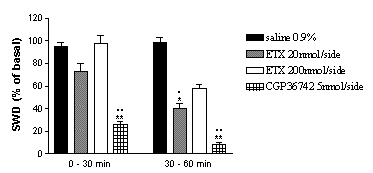
Figure
1: Effect of direct infusion of either ETX, CGP 36742 or saline into the
ZI, on SWD in GAERS. Drug effects were assessed by repeated measures ANOVA,
with post-hoc comparison to basal values using Dunnet's test when significant
(* p<0.05 & ** p<0.01) as well as by an unpaired Students t-test
in comparison to the vehicle at the same time point (![]() p< 0.05 &
p< 0.05 & ![]()
![]() p<0.011).
n = 4 for each dose.
p<0.011).
n = 4 for each dose.
Infusion of 20nmol/side of ETX failed to produce an immediate cessation of seizure activity, as has been demonstrated after systemicadministration (50mg/kg) (Richards et al., 2003). A moderate (~50%) decrease in SWD activity was seen in the second post infusion recording period. A similar trend was observed after infusion of 200nmol/side of ETX, although the delayed decrease did not reach significance. Infusion of 0.9% saline had no effect on seizure activity. CGP 36742 infusion caused a pronounced reduction in seizure activity in both the first and second post infusion recording periods. These results suggest that the ZI may have a similar influence on SWD to that of the nRT (Richards et al., 2003), since both regions GABAergically innervate the TC.
Barthó
P. et al., (2002) Eur. J. Neurosci 16, 999-1014.
Coulter D.A., et al., (1989) Ann. Neurol 25, 582-583.
Danober L. et al., (1998) Prog. Neurobiol 55, 27-57.
Meeren H.K.M. et al., (2002) J. Neurosci 22(4), 1480-1495.
Richards D.A., et al., (2003) Epilepsy Res 54, 97-107.