| pA2 online © Copyright 2004 The British Pharmacological Society |
003P
GKT, University of London Winter Meeting December 2003 |
|
Effects
of chronic treatment with ß-adrenoceptor ligands on a murine
model of asthma |
|
ß-blockers are currently contraindicated in the treatment of asthma due to their deleterious acute effects. The clinical effects of treatment with ß-adrenoceptor (ß-AR) agonists and antagonists in heart failure vary with duration of therapy, as do the effects of ß-AR agonists in asthma. Therefore, we hypothesized that chronic effects of 'ß-blockers' in asthma may differ from those observed acutely.
Ovalbumin-sensitized and -challenged Balb/cJ mice (male, 20-25g) (Sensitized) were treated for either 28 days (chronic) or 15 min (acute) with salbutamol (SAL, n=10-9 animals; chronic: 0.5 mgkg-1 day-1 s.c. / acute: 0.15 mgkg-1 i.v.), alprenolol (ALP, n=9-18 animals; chronic: 7200 ppm p.o. / acute: 72 mgkg-1 i.v.), nadolol (NAD, n=9-13 animals; chronic: 250 ppm p.o. / acute: 72 mgkg-1) or carvedilol (CAR, n=8-15 animals; chronic: 2400 ppm p.o./ acute: 24 mgkg-1 i.v.) before measuring airway responsiveness to the muscarinic agonist methacholine. Sensitized and control (Ctrl, non-sensitized/non-challenged) mice (n=6-25 animals) were treated with vehicle. Airway resistance (Raw) was measured using the forced oscillation technique (Evans et al., 2003) (Figure 1). ß-AR density was measured in membranes prepared from lung tissue using the ß-AR radioligand 125I-ICYP (5 - 7500 pM) (Table 1). The specific binding was saturable and in all cases displayed a Hill coefficient not different from unity.
Fig. 1 and Table
1 illustrate that CAR and NAD exhibited different acute and chronic effects
on both methacholine induced increases in Raw
and Bmax values, and showed opposing
effects to SAL and ALP. Surprisingly, both chronic CAR and NAD decreased
Raw.
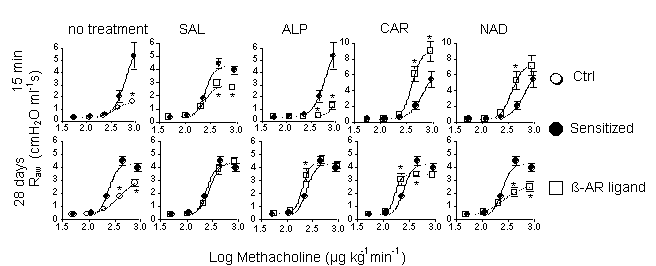
Figure 1: 15 min infusion of ß-AR ligand either significantly reduced (SAL and ALP) or increased (CAR and NAD) Raw (*P<0.05, ANOVA) compared to Sensitized. 28 d treatment with CAR and NAD significantly decreased Raw while SAL and ALP had no effect. Please note changes in y-axis for acute CAR and NAD. Values are mean±s.e.m.
| Treatment |
15
minutes
|
28
days
|
||
| Ctrl |
286.8
± 88.02
|
*
|
286.8 ± 88.02
|
|
| Sensitized |
109.2
± 9.72
|
109.2
± 9.72
|
||
| Salbutamol |
256.5
± 29.24
|
*
|
97.0
± 23.02
|
|
| Alprenolol |
299.5
± 12.19
|
*
|
179.2
± 53.05
|
|
| Carvedilol |
86.3
± 19.42
|
904.1
± 43.46
|
*
|
|
| Nadolol |
181.9
± 48.28
|
785.5
± 154.8
|
*
|
|
Table 1: 15 min treatment with SAL or ALP significantly increased Bmax (fM mg-1 protein) to Ctrl values, while 28 d with CAR or NAD increased Bmax values significantly for ß-AR receptors in lung membranes. Values are mean±s.e.m. of n=3-5 animals in each group (*P<0.05 comp. to Sensitized, Student's t-test). Samples were run in triplicate.
Evans, K.L., et al. (2003). J Appl Physiol, 94, 245-52.
The presented work was supported by grants from NIH, AHA, Sandler Program for Asthma Research and GlaxoSmithKline.