| pA2 online © Copyright 2004 The British Pharmacological Society |
024P
GKT, University of London Winter Meeting December 2003 |
|
Role of
toll- like receptors 2 and 4 in vascular responses |
Search PubMed for: Harrington LS Mitchell JA |
Toll-like receptors (TLR) are known to be involved in pathogen sensing (Medzhitov et al., 1997). At present, 10 TLR isoforms have been described in mammals, which respond to different pathogenic ligands principally via the NF?B signalling pathway. The variety of these receptors and the means by which they are stimulated may reflect the type of inflammatory response initiated. However, both TLR2 and TLR4 are present on endothelial cells and therefore may have a direct role in vasomotor responses of vessels. This possibility has thus far not been investigated. Here we have compared vasoconstrictor and vasodilator responses in mesenteric vessels from control mice with those of mice deficient in TLR4 (TLR4-/-) or TLR2 (TLR2-/-).
TLR2 -/- and TLR4 -/- mice, generated by gene targeting, were obtained via collaboration (Takeuchi et al., 2000), and male C57BL/6 mice were used as wild type controls. Mice were killed by lethal exposure to CO2 followed by cervical dislocation. Second order mesenteric arteries were mounted in myographs and vasomotor responses recorded. Tissues were immersed in physiological salt solution (PSS), equilibrated (30 min) and tensions normalised as described previously (Mulvany and Halpern, 1977). Concentration response curves to methoxamine (3x10-8 - 3x 10-4M) are shown as Force (mN). Vasodilation in response to acetylcholine (3x10-8 - 3x 10-4M) was measured in U46619 (3x10-8 M) pre-contracted arteries and calculated as % of induced tone.
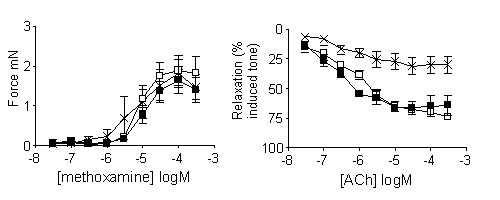
Figure 1: Constrictor
(left side) and dilator (right side) effects of methoxamine and acetylcholine
(ACh) in mesenteric vessels from control (![]() ),
TLR2-/- (
),
TLR2-/- (![]() )
or TLR4-/- (X) mice. Data is shown as
the mean ± s.e.m. for n=4 experiments.
)
or TLR4-/- (X) mice. Data is shown as
the mean ± s.e.m. for n=4 experiments.
Contractile responses to methoxamine were comparable in arteries from control, TLR2-/- or TLR4-/- mice (Figure 1). However, endothelium-dependent vasodilation in response to acetylcholine was considerably impaired in TLR4-/- mice but not TLR2-/- mice (figure 1).
It is known that TLR4 receptors are expressed on endothelial cells. Our current data suggests that they have a role in maintenance of endothelial function.
Takeuchi
et al. (2000). J. Immunol; 165: 5392-6.
Medzhitov et al. (1997). Nature; 388: 394-7.
Mulvany &
Halpern (1977) Circ Res 41:19-26.
This work was funded by the British Heart Foundation.