| pA2 online © Copyright 2004 The British Pharmacological Society |
064P
GKT, University of London Winter Meeting December 2003 |
|
Effects
of intraplantar injection of n-arachidonoyl-dopamine on mechanically
evoked responses of dorsal horn neurones in anaesthetised rats |
|
N-Arachidonoyl-dopamine (NADA) activates cannabinoid (CB1) receptors and vanilloid receptors (VR1) (Bisogno et al., 2000). Here, effects of intraplantar injection of NADA on ongoing and mechanically (8-100g) evoked responses of dorsal horn neurones of the spinal cord were studied in rats.Extracellular recordings of wide dynamic range dorsal horn neurones were made in isofluorane-anaesthetised rats in vivo.
Effect of peripheral injection of NADA (5µg/50µl) on mechanically-evoked responses was studied.
The ability of pre-treatment with CB1 receptor antagonist SR141716 (0.01µg/50µl) or the VR1 receptor antagonist iodo-resiniferatoxin (I-RTX; 0.3773µg/50µl) to block the effects of NADA was studied.
Peripheral injection of NADA (5µg/50µl) significantly inhibited mechanically-evoked responses (8-100g) compared to vehicle (n=7 neurones, 7 rats; figure 1). Effects of NADA on 8, 10 and 15g mechanically evoked responses were blocked by pre-administration of SR141716A (0.01µg/50µl). SR141716A did not block the inhibitory effect of NADA on 26-100g -evoked responses of DH neurones (figure1). Pre-administration of I-RTX (0.3773µg/50µl) significantly reduced the inhibitory effect of NADA on 10, 15, 26, 100g -evoked responses of dorsal horn neurones.
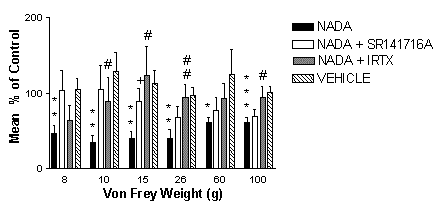
Fig. 1 Effects of peripheral injection of NADA (5µg/50µl) alone, after pre-treatment with SR141716A (0.01µg/50µl), IRTX (0.3773µg/50µl) or vehicle on mechanically-evoked responses of dorsal horn neurones. Data are presented as mean maximal % control ± SEM. Statistical analysis comparing NADA (5µg/50µl) and vehicle performed with Mann Whitney test * p <0.05, ** p<0.01, ***p<0.001. Comparisons between effects of NADA (5µg/50µml) alone and after pre-treatment with SR141716A (0.01mg/50ml) performed with Mann Whitney test, + p< 0.05. Comparisons between NADA (5µg/50µl) alone and after pre-treatment with I-RTX (0.3773µg/50µl) performed with Mann Whitney test, # p< 0.05, ## p<0.01.
Our data suggest that NADA inhibits low intensity, innocuous responses of dorsal horn neurones via activation of CB1 receptors whereas actions at CB1 and VR1 receptors mediate the effects of NADA on high intensity, noxious evoked responses.
Bisogno T. et al (2000) Biochem J., 351, 81.
This study was supported by BBSRC and GlaxoSmithKline.