| pA2 online © Copyright 2004 The British Pharmacological Society |
102P
GKT, University of London Winter Meeting December 2003 |
|
Glucocorticoids
inhibit IL-4- and IL-13-stimulated proliferation of rat primary
airway fibroblasts |
|
Subepithelial fibrosis is one of the features of airway remodelling which occurs in the course of allergic asthma (Roche et al., 1989). Since Th2 cytokines and in particular IL-4 and IL-13 play a key role in the pathogenesis of allergic asthma (Wills-Karp, 1999), the effects of these cytokines on primary airway fibroblasts in culture were studied. Very recently, we observed that in airway fibroblasts arginase, which provides the substrate for collagen synthesis, is markedly up-regulated by IL-4 and IL-13 (Lindemann & Racké, 2003). Here, the effects of these cytokines on the proliferation of airway fibroblasts was studied.
Primary airway fibroblasts were obtained from isolated trachea of Sprague Dawley rats of either sex (160-200 g) by an outgrowth technique in the presence of fetal calf serum (FCS, 10%). (Lindemann & Racké, 2003). Passages 2-3 were used for experiments. After trypsinisation, the cells were disseminated (0.25*106 cells well-1) and cultured for 24 h in DME/F-12 medium containing 10% FCS followed by 24 h culture in the absence of FCS. Thereafter, the cells were cultured for an additional 24 h (test period) in the absence or presence of FCS, or test substances and the additional presence of [3H]-thymidine (10 µM, 1 µCi).
When FCS was present or absent during the test period, the incorporation of [3H]-thymidine amounted to 4 011 ± 863 d.p.m. (n=29) and 976 ± 113 d.p.m (n=16), respectively (means ± s.e.mean; p<0.001).
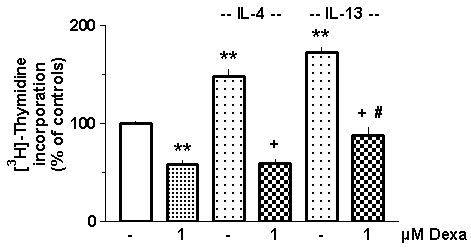
Figure 1. Effects of dexamethasone (Dexa, 1 µM) and/or IL-4 (10 ng ml-1) and/or IL-13 (10 ng ml-1) on [3H]-thymidine incorporation in airway fibroblasts cultured in the absence of FCS. Given are means±s.e.mean of n³12. ** P<0.01 vs controls; + P<0.01 vs respective value in the absence of Dexa; # P<0.05 vs Dexa alone. Statistical analysis was performed by ANOVA followed by Bonferroni.
Figure 1 shows that IL-4 and IL-13 caused a clear stimulation of airway fibroblast proliferation. Dexamethasone which alone inhibited [3H]-thymidine incorporation by about 45%, prevented the stimulatory effect of IL-4 and largely attenuated that of IL-13.
In conclusion, in parallel to their effects on arginase (Lindemann & Racké, 2003) Th2 cytokines stimulate proliferation of airway fibroblasts in a glucocorticoid-sensitive manner.
Lindemann, D. &
Racké, K. (2003) Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch. Pharmacol.,
368, 546-550.
Roche, W.R. et al. (1989) Lancet, 1(8637), 520-524.
Wills-Karp, M. (1999) Annu. Rev. Immunol., 17,255-281.