| pA2 online © Copyright 2004 The British Pharmacological Society |
211P
GKT, University of London Winter Meeting December 2003 |
|
Zolmitriptan
demonstrates good pharmacokinetic consistency between and within
individuals following intranasal administration |
|
Zolmitriptan nasal spray is a very fast acting acute migraine treatment that has demonstrated consistent, high efficacy in clinical trials (Aschoff et al. 2003; Dowson et al., 2003).
The aim of the study was to determine the variability between and within individuals of pharmacokinetic data for both zolmitriptan and its active N-desmethyl metabolite 183C91, following administration of zolmitriptan nasal spray 5 mg.
Healthy adult volunteers
(n=18) received a single intranasal dose of zolmitriptan 5 mg on each
of 3 occasions (separated by washout periods of ![]() 70
hours and
70
hours and ![]() 2 weeks).
Blood samples were collected 30 minutes before dosing and from 2 minutes
to 16 hours post-dose. Zolmitriptan and 183C91 plasma concentrations were
determined by liquid chromatography and electrospray mass spectrometry.
The estimations of intra- and inter-subject variation were performed using
an ANOVA mixed linear model including terms for fixed effects of gender
and period.
2 weeks).
Blood samples were collected 30 minutes before dosing and from 2 minutes
to 16 hours post-dose. Zolmitriptan and 183C91 plasma concentrations were
determined by liquid chromatography and electrospray mass spectrometry.
The estimations of intra- and inter-subject variation were performed using
an ANOVA mixed linear model including terms for fixed effects of gender
and period.
Quantifiable plasma
concentrations of zolmitriptan (![]() 0.1
ng/ml) were measured in 16/18 patients at 2 minutes in at least one of
the periods. Mean plasma concentrations were similar in each of the periods
(Figure 1). Coefficients of variation for AUC were 35.3% between volunteers
and 21.6% within volunteers for zolmitriptan, and 25.5% and 22.8%, respectively,
for 183C91.
0.1
ng/ml) were measured in 16/18 patients at 2 minutes in at least one of
the periods. Mean plasma concentrations were similar in each of the periods
(Figure 1). Coefficients of variation for AUC were 35.3% between volunteers
and 21.6% within volunteers for zolmitriptan, and 25.5% and 22.8%, respectively,
for 183C91.
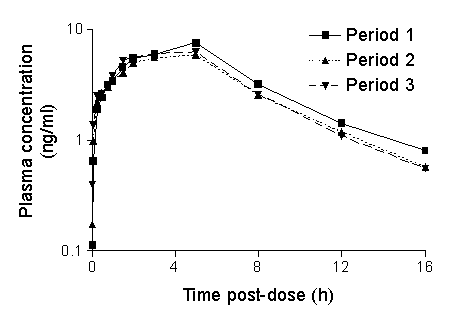
The level of pharmacokinetic variability within and between individuals was low, with variability estimates for zolmitriptan and 183C91 AUC within individuals being even lower. This observation may explain the consistent efficacy of zolmitriptan over multiple attacks that has been reported in clinical studies.
Aschoff J et al.
(2003) Cephalalgia, 23: 711
Dowson AJ et al. (2003) CNS Drugs, 17: 839-851.