| pA2 online © Copyright 2004 The British Pharmacological Society |
035P
University of Newcastle Winter Meeting December 2004 |
Effects of spinal UCM707 and anandamide on evoked responses of dorsal horn neurones in anaesthetised rat V.Chapman1, D.R. Sagar1, E. de Lago3, J. Fernandez-Ruiz3, C.T. O’Shaughnessy2, D.A.Kendall1. 1University of Nottingham, UK, 2Neurology & GI CEDD , GSK, Harlow, UK, 3Facultad de Medicina, Universidad Complutense, Madrid, Spain. |
|
Anandamide is an endogenous ligand at both cannabinoid (CB1) and vanilloid (TRPV1) receptors. UCM707 is a potent and selective inhibitor of the putative endocannabinoid transporter (López-Rodríguez et al., 2001). Here, effects of spinal administration of anandamide (AEA) and UCM707, alone or in combination, on mechanically-evoked responses of dorsal horn (DH) neurones of the rat spinal cord were studied.
Extracellular recordings of wide dynamic range DH neurones were made in anaesthetised rats in vivo. Effects of spinal application of AEA (5µg/50 µl; n=6), UCM707 (10µg/50µl; n=6), alone or in combination, on mechanically- (10-100g) evoked responses of DH neurones were studied. AEA significantly inhibited mechanically-evoked responses (10-100g) compared to vehicle (n=6 neurones, 6 rats; figure 1). UCM707 (10µg/50µl) also significantly inhibited mechanically-evoked responses of DH neurones compared to vehicle (Figure 1). Co-administered AEA and UCM707 did not, however, alter mechanically-evoked responses of DH neurons compared to application of vehicle.
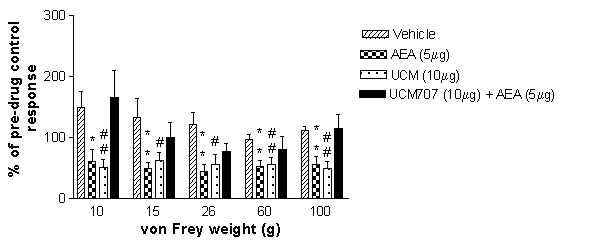
Figure 1. Effects of spinal administration of AEA (5µg/50µl) and UCM707 (10µg/50µl) alone, or in combination, and vehicle on mechanically-evoked responses of DH neurons. Data are presented as mean maximal percentage control. Statistical comparisons between effects of AEA (5µg/50µl) and vehicle: Mann-Whitney test * p<0.05, **p<0.01. Comparison between UCM707 (10µg/50µg) and vehicle: Mann-Whitney test #p<0.05, ##p<0.01.
These data demonstrate that spinal administration of the endocannabinoid anandamide and UCM707 have a similar inhibitory effect on innocuous and noxious mechanically-evoked responses of DH neurones. Co-administration of anandamide and UCM707 did not, however, inhibit mechanically-evoked responses of spinal neurones. The basis for this lack of effect is unknown and requires further investigation. This study was supported by BBSRC and GlaxoSmithKline.
López-Rodríguez, M.L. et al., (2001) J. Med. Chem., 44 , 4505–4508 .
This study was supported by BBSRC and GlaxoSmithKline.