| pA2 online © Copyright 2004 The British Pharmacological Society |
052P
University of Newcastle Winter Meeting December 2004 |
In-vivo analysis of icilin as a chemical modulator of TRPM8 and TRPA1, the cold sensing receptors Jennifer L Mills, David A Kendall & Victoria Chapman, School of Biomedical Sciences, University of Nottingham, Nottingham NG7 2UH, UK. |
|
Previous in-vitro studies have shown that cells expressing either TRPM8 or TRPA1 are activated by cool temperatures (threshold 23 °C and 17 °C respectively) and the potent cooling compound icilin (McKemy et al., 2002; Story et al., 2003). The aim of this study was to investigate the potential use of icilin as an activator of cold sensing receptors in vivo. Here we determined the effects of peripheral injection of icilin (5 µg/50 µl and 10 µg/50 µl) on responses of wide dynamic range (WDR) neurones in rats.
Ex tracellular single-unit recordings of deep (500-1000 µm) dorsal horn WDR neurones were made in isoflurane anaesthetised Sprague-Dawley rats (n=28; weight 250-300g). Mechanically sensitive WDR neurones were located by brush or pinch stimuli, characterised with transcutaneous electrical stimulation (3 times threshold) and mechanical punctate stimulation. Cold responsive dorsal horn WDR neurones responded (spikes/s) to the application of ice to the receptive field. Effects of intraplantar injection of 5 µg/50 µl icilin, 10 µg/50 µl icilin or vehicle (3% DMSO, 3% Tween 80 and 94% saline) on the firing of WDR neurones were determined.
WDR neurones responded to mechanical stimulation of the hindpaw. Intraplantar injection of 10 µg/50 µl icilin significantly increased firing of WDR neurones (n=7), compared to vehicle (n= 9: Figure 1). The lower dose of icilin studied (5 µg/50 µl) showed a similar trend (n=7), however effects were not significant compared to vehicle. Application of ice to the peripheral receptive field produced a significant increase in firing of WDR neurones, compared to control (Student t-test, p<0.0001). All ice responsive WDR neurones tested responded to icilin (n= 5 neurones).
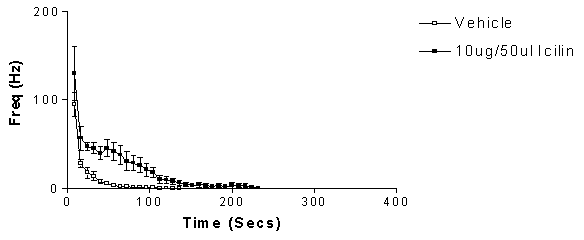
Figure 1: Comparison of the effects of intraplantar injection of icilin versus vehicle on firing of WDR neurones in anaesthetised rats. Area under the curve analysis revealed a significant difference between the effect of icilin and vehicle (Mann-Whitney, p<0.05).
Thus, both intraplantar injection of icilin and local application of ice produce a significant increase in WDR neurone firing. These data support the use of icilin as a chemical modulator to characterise further the role of the cold sensing receptors, TRPM8 and TRPA1 in cold nociceptive processing.
McKemy et al., (2003) Nature, 416, 52-8.
Story et al., (2003) Cell 112, 819-29.
This study was supported by the MRC.