| pA2 online © Copyright 2004 The British Pharmacological Society |
053P
University of Newcastle Winter Meeting December 2004 |
Effect of a novel small molecule antagonist of the integrin very late antigen-4 in murine collagen induced arthritis Alexander Vugler, Adrian Moore, Neil Gozzard and Roland Foulkes. Celltech R & D, 208 Bath Road, Slough, Berkshire SL1 3WE, UK. |
|
Lymphocytes are central to inflammation and are mediators of tissue damage in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). The integrin Very Late Antigen-4 (VLA-4) is expressed on lymphocytes and binds vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) and fibronectin connecting segment-1 (CS-1), both being expressed in RA synovium (van Dinther-Janssen et al, 1991 & Muller-Ladner et al, 1997). Infiltration of lymphocytes into the joint is mediated in part via VLA-4. In two separate experiments the effect of a novel VLA-4 antagonist, CT7429 (Figure 1) and leflunomide (a clinically used antirheumatic agent) on murine collagen induced arthritis (CIA) were examined.
Male DBA/1 mice (20-25g) were sensitised to chick sternal type II collagen (100 µg) in complete Freunds adjuvant intradermally at the base of the tail. 14 days later animals were boosted with chick collagen II in incomplete Freunds adjuvant. Compound was administered prophylactically 1 day prior to sensitisation. Leflunomide was dosed p.o. (100 µl) once daily at 3mg/kg in 1% methylcellulose. CT7429 dosed p.o. (100 µl) b.i.d. at 50mg/kg in 4% 1- methyl 2-pyrrolidone and 96% labrafil. Once signs of arthritis were observed animals were scored and weighed daily (day 12-36). CIA was scored on a 1-3 scale per paw. 1 = wrist/ankle affected. 2 = 1+ pad affected. 3 = 2+ digits affected. At termination blood samples were taken for pharmacokinetic analysis and limbs for histopathological analysis to assess cellular infiltration and tissue integrity on a 1-3 scale.
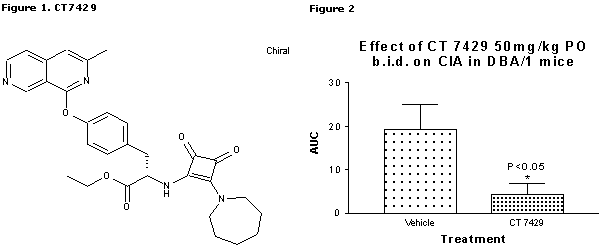
Data were analysed using the Mann Whitney test. Chi-square test was used on incidence. Data are expressed as mean ± s.e.m. P<0.05 considered significant (CT7429 n=27; Vehicle n=27; Leflunomide n=15; Vehicle n=15).
Administration of CT7429 caused a significant reduction in area under the curve (AUC) of the clinical score from 19.20 ±5.75 to 4.33 ±2.40, P<0.05 (Figure 2) as compared to vehicle. CT7429 also caused a significant inhibition in incidence and histopathological score, from 56 to 27% (P<0.05) and from 1.19 ±0.10 to 0.78 ±0.09 (P<0.01). Plasma levels of the active compound were 208 ±77.50 ng/ml (n=4) 4 hours post dose. Leflunomide caused a significant reduction in AUC from 40.20 ±8.46 to 12.83 ±5.11 (P<0.05) with a corresponding inhibition of incidence from 80 to 40%. Leflunomide also caused a significant decrease in histopathological score from 1.48 ±0.11 to 1.08 ±0.10 (P<0.01).
These data indicate that the novel small molecule VLA-4 antagonist, CT7429, significantly inhibits CIA in DBA/1 mice and has comparable effects to leflunomide.
Muller-Lander et al, 1997. Journal of Rheumatology. 24: 1873-80.
Van Dinther-Janssen et al, 1991. Journal of immunology. 147: 4207-10.