| pA2 online © Copyright 2004 The British Pharmacological Society |
069P
University of Newcastle Winter Meeting December 2004 |
The hypophagic effect of 8-OH-DPAT in hungry rats is mediated by an action at 5-HT1A receptors M.J. Arkle & I.S. Ebenezer. Neuropharmacology Research Group, School of Pharmacy and Biomedical Sciences, University of Portsmouth, Portsmouth, PO1 2DT, U.K. |
|
It has been previously shown that while the 5-HT1A receptor agonist 8-hydroxy-2-(di-N-propylamino)-
tetralin (8-OH-DPAT) increases food intake in non-deprived rats by an action at 5-HT1A autoreceptors (see Fletcher et al., 1996), it decreases feeding in food-deprived animals (Ebenezer, 1992). The mechanism by which the 5-HT1A receptor agonist inhibits feeding in fasted animals is not known (Ebenezer, 1992). However, it has recently been found that 8-OH-DPAT is also an agonist at 5-HT7 receptors (Hoyer et al., 2002) and it is possible that some of the its behavioural effects are mediated by an action at these receptors. The present study was therefore undertaken to investigate whether the hypophagic effect of 8-OH-DPAT in fasted rats is mediated by an action at 5-HT1A receptors.
Male Wistar rats (n=32, b.wt. 260 - 300g) were fasted for 22h, and injected with either saline followed by saline (n=8), saline followed by 8-OH-DPAT (50 μg kg-1; n=8), the 5-HT1A receptor antagonist WAY 100635 (0.3 mg kg-1) followed by saline (n=8), WAY 100635 (0.3 mg kg-1) followed by 8-OH-DPAT (50 μg kg-1; n=8). Both injections were given s.c.; 30 min separated the 2 injections. Immediately after the second injection, the rats were placed separately in experimental cages with access to food. Food consumption was measured at intervals over 120 min, as described previously (Ebenezer, 1990). The data were analysed by two-way ANOVA and post-hoc Dunnett’s test.
The results are illustrated in Fig. 1. In agreement with previous results, 8-OH-DPAT (50 μg kg-1) significantly reduced food intake in the fasted rats (Ebenezer, 1990). The selective 5-HT1A receptor antagonist WAY 100635 (Fletcher et al., 1996) had no effect on food intake. However, pretreatment with WAY 100635 (0.3 mg kg-1) completely abolished the hypophagic effect of 8-OH-DPAT. The results of this study extend previous observations and suggest that the suppressant effect of 8-OH-DPAT on food intake in food-deprived rats is mediated by an action at 5-HT1A receptors.
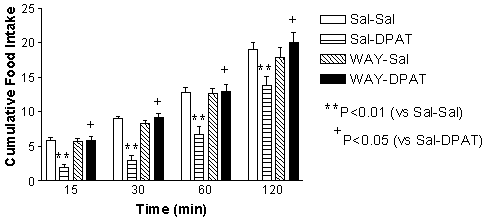
Fig. 1. The effect of WAY100635 (0.3 mg kg-1) on the hypophagic effect of 8-OH-DPAT (50 μg kg-1; DPAT) in 22h food-deprived rats. Vertical line rep. + s.e.mean.
Ebenezer, I.S. (1990) NeuroReport, 1, 73 – 76.
Ebenezer I.S. (1992) NeuroReport, 3, 1019-1022.
Fletcher, A. et al. (1996) Behav Brain Res., 73, 337 – 353.
Hoyer, D. et al. (2002) Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav., 71, 533 – 554.