| pA2 online © Copyright 2004 The British Pharmacological Society |
107P
University of Newcastle Winter Meeting December 2004 |
Pharmacological characterisation of secretin species homologues at the human recombinant secretin receptor I.D. Cousins1, J. Picot2, T. Evans2, R.A.Coleman1, K.L.Clark1 & R.J. Davis1. 1Pharmagene Laboratories Ltd, Orchard Rd, Royston, Herts. SG8 5HD. 2University of Glasgow, Western Infirmary, Glasgow. G11 6NT. |
|
The secretin receptor (SCTR) is a Gs-coupled receptor that is positively coupled to adenylyl cyclase and elevates cAMP upon agonist stimulation. Its native agonist is secretin, a 27 amino acid duodenal peptide, the sequence of which differs between species. In comparison to human secretin, other mammalian secretin homologues exhibit between 1 and 4 amino acid substitutions at positions 5, 14, 15 and 16, while avian (chicken) secretin contains only 14 conserved residues. In the present study we compared the potencies of all commercially available mammalian and avian secretin homologues at the human recombinant SCTR.
HEK-293 cells stably transfected with the human SCTR were cultured to confluence in 96-well plates in a 37 oC, 5%CO2 incubator. Culture media was MEM supplemented with 10% foetal bovine serum, 100U/ml penicillin, 100ng/ml streptomycin, 2.5 µg/ml fungizone, 2mM glutamine, and 600 µg/ml geneticin (G418). Cells were stimulated by secretin species homologues (10-11 to 10-7 M) for 15 minutes in the presence of 1µM IBMX, before assay termination with 1M HCl. Stimulated cAMP levels were determined from a standard curve in a radioligand displacement binding assay.
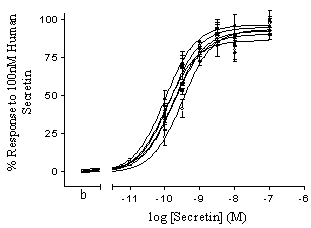
Human secretin caused a concentration-dependent elevation of cAMP, with a mean pEC50 of 9.9 ± 0.2M (0.13nM). Similarly, concentration dependent elevations in cAMP accumulation were also observed in response to all other species variants of secretin tested. Statistical analyses were carried out by one-way ANOVA, where p<0.05 was taken to indicate statistical significance. No significant differences in maximum response or potency were observed between the different homologues of secretin tested (Figure 1; Table 1). Human secretin failed to raise cAMP accumulation above basal levels in null transfected HEK-293 cells.
 |
|
Figure and Table 1. Functional potency (cAMP response) of species homologues of secretin. Data (mean ± s.e.mean) are expressed as percentage of the maximal response exhibited by 100nM human secretin, (n=3).
In conclusion, these data demonstrate that when transfected into HEK293 cells, the human recombinant SCTR is functionally coupled to cAMP accumulation. Furthermore, we can conclude that in this test system, there are no differences in potency or maximum cAMP response between the mammalian and avian secretin homologues evaluated.