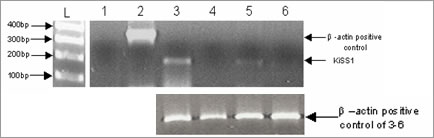
Discovery of novel orphan G-protein-coupled receptor KISS1R and ligand Kp-10 expression in human cardiovascular system The orphan G-protein coupled receptor KISS1R (GPR54, AXOR12, hot7t175) was paired with products of the KiSS-1 gene in 2001 (Ohtaki et al., 2001). Four biologically active cleavage products of the KiSS-1 gene, kisspeptin (Kp)-54 (metastin), Kp-14, Kp-13 and Kp-10, were identified as metastasis suppressors (Lee et al., 1996). KiSS-1 peptide has been implicated in placentation and as a molecular switch in puberty (Seminara et al., 2003). The physiological role of this receptor system within the diseased and normal human cardiovascular system is not yet known, although effects upon migration of cells and interaction with the gelatinases suggest a role in angiogenesis or vascular remodelling as opposed to a vasodilator/vasoconstrictor action. Therefore we hypothesise that the KISS1R/KiSS-1 peptides will have a role within the human cardiovascular system. However to date distribution of the peptide and receptor has not previously been characterised in these tissues. Our aims therefore were to elucidate the cardiovascular distribution of KISS1R and its ligand Kp-10 using reverse transcription – polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and immunocytochemistry (ICC). Immunocytochemical localisation of KISS1R and Kp-10 was performed on 30μm sections stained using anti-KISS1R(375-398) (human) serum or anti-Kp-10-NH2 (human) serum and detected using a peroxidase/antiperoxidase protocol (Kuc., 2002). Vessels were cleaned of connective tissue and messenger RNA (mRNA) extracted using Invitrogen Micro-FastTrack 2.0 Kit. Synthesis of cDNA was carried out using the Invitrogen SuperScript III First-Strand Synthesis System for RT-PCR and oligo dT primer. RT-PCR analysis was carried out with KISS1R specific primers sense 5’ –TGTACAACCTGCTGGCGCTG - 3’ and anti-sense 5’ – CCACTGCTCCCTGGCTTCTG - 3’ . KISS1R and Kp-10 immunoreactivity was detected in endothelial cells of radial artery. Additionally KISS1R was observed in the endothelial cells of histologically normal saphenous vein and failed saphenous vein graft (SVG). KISS1R mRNA was detected in SVG with the endothelial layer intact, but not in SVG with the endothelial layer removed. Kp-10 was only specifically detected in endothelial cells of SVG, not SV.
This study has demonstrated for the first time the presence of KISS1R and Kp-10 within human vasculature. Kuc, (2002) Methods in Molecular Biology 206, 10-18. |