Print version
Search Pub Med
The calcium channel α2/δ-1 subunit modulates directly plasma membrane expression of T-type calcium channel Cav3/ α1 subunits
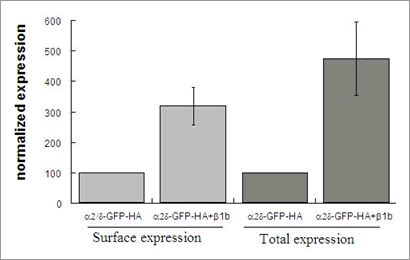
The gabapentin/pregabalin binding calcium channel subunit α2/δ-1 has recently become a focus in the treatment of neuropathic pain. Increases in α2/δ-1 mRNA levels in various neuropathic models have been reported. It has also been suggested that the auxiliary subunits (β and α2/δ) of high voltage-activated (HVA) calcium channels modulate CaV3 subunits of T-type, low voltage-activated (LVA) calcium channels. Such a regulation has yet to be documented, especially because there has been no biochemical characterization of T-channels. To monitor total protein levels and plasma membrane expression of T-channels in living cells, external epitopes (hemagglutinin, FLAG) were introduced into human recombinant CaV3 subunits that were also N-terminally fused to GFP. Utilizing Western blot techniques, fluorescence flow cytometry, immunofluorescence, luminometry, and electrophysiology, we found that b 1b and α2/δ-1 subunits enhance the level of CaV3 proteins as well as their plasma membrane expression in various expression systems. We also report that, in both Xenopus oocytes and mammalian cells, the α2/δ-1 and and β1b subunits increased by at least 2-fold the T-current density with no change in the electrophysiological properties. Subsequently, using a N-terminal HA-GFP tagged α2/δ-1 subunit, we now show that β1b is able to increase both total and plasma membrane expression of α2/δ-1 suggesting that synergistic increases of calcium channel expression is brought about by the action of β subunits on α2/δ-1 expression. Altogether, these data indicate that 1) both the β subunits and the gabapentin/pregabalin a2/δ-1 binding subunit are able to modulate CaV3 subunit surface expression, and (2) that β subunits modulate the expression of α2/δ-1.
Altogether, the data indicate that the membrane targeting of the calcium channel CaV subunits is regulated dynamically through the expression of both β1b and α2/δ-1 subunits and further suggests that alteration in α2/δ-1 expression may impact the expression of both HVA and LVA calcium channels in neuropathic conditions. Abe, M., Kurihara, T., Han, W., Shinomiya, K & Tanabe, T. (2002) Spine 27, 1517-1524; discussion 1525. |