MDMA increases TNF-α mRNA expression in rat brain by a mechanism involving hyperthermia
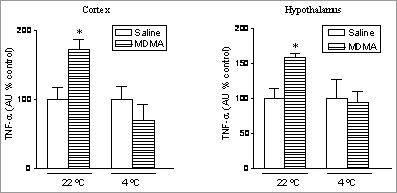
Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) plays a pivotal role in inflammation and apoptosis and is a mediator of several forms of degenerative disorders in rodent brain (Venters et al., 2000). 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, ‘ecstasy’) acutely increases IL-1β levels in rat brain and i.c.v. IL-1β injection enhances the MDMA-induced hyperthermia and neurotoxicity (Orio et al., 2004; O’Shea et al., in press). We have now examined the time-course of changes induced by MDMA on TNF-α mRNA levels in the rat cortex and hypothalamus and investigated whether these changes are related to the hyperthermia subsequent to MDMA. Adult male Dark Agouti rats (150-175 g) housed at a room temperature of 22ºC received MDMA (12.5 mg kg-1, i.p.) or saline and were killed 1 h, 3 h, 6 h, 9 h, 12 h and 24 h later. TNF-α mRNA expression was determined by RT-PCR (Yu et al., 2004). A group of rats was maintained at 4ºC for 4 h before and up to 6 h after drug administration, time at which animals are killed me. Rectal temperature was measured throughout. MDMA produced an increase in the TNF-α mRNA expression in cortex and hypothalamus 6 h after administration (Figure 1). An apparent increase in cortical TNF-α mRNA expression was observed 3 h after MDMA, but differences were not significant. No change was observed 1 h, 9 h, 12 h or 24 h after drug injection. When rats were kept at 4ºC the rise in both, body temperature and TNF-α mRNA expression was abolished. These findings indicate that MDMA induces an acute increase in the brain TNF-α mRNA expression which is related to the hyperthermic response and suggest that TNF-α could be involved in the neuronal damage induced by the drug.
Figure 1. Effects of ambient temperature on the TNF-α mRNA expression in cortex and hypothalamus after MDMA (12.5 mg/kg, i.p.) injection. Rats were kept at 4ºC for 4 h before and up to 6 h after MDMA, time at which animals were killed. Blots show the products of RT-PCR for TNF-α (295 bp) and β-actin (200 bp). Results shown as mean ± s.e.mean, n= 4-6. Different from saline: *P<0.05 (one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey´s test). AU: arbitrary units. S: saline; M: MDMA. Orio, L., et al., (2004). J. Neurochem . 89: 1445-1453. M.I.C. thanks MCYT (SAF2004-02603) and FIS (G03-005) for support. |