Print version
Search Pub Med
Heat shock preconditioning protects against MDMA-induced 5-HT neurodegeneration in the dark agouti rat
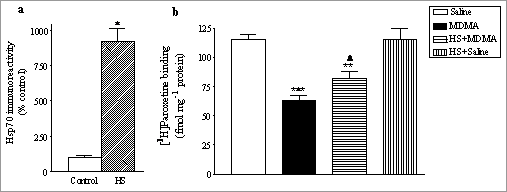
Preconditioning involves exposure to a sub-threshold insult in order to trigger a powerful endogenous protective mechanism which lessens the impact of a subsequent, more severe challenge (Dirnagl et al., 2003). Heat shock protein 70 (Hsp70) is thought to participate in the development of this tolerance (Sato & Matsuki, 2002). 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, ‘ecstasy’) produces long-term 5-HT nerve terminal damage in rats which is modulated by the hyperthermic response produced by the drug (Green et al., 2003). We have now examined if increased Hsp70 levels induced by prior heat shock (HS) protect against MDMA-induced 5-HT neurodegeneration. Once daily for 4 days, the rectal temperature of adult male Dark Agouti rats (160-180 g) was raised to and maintained at 41.5ºC for 1 h by exposure to an elevated ambient temperature (30ºC) while on a heating blanket (HS). Twenty-four h after the 4th HS, separate groups of animals were either killed and Hsp70 expression determined in cerebral cortex by Western blot or treated with MDMA (12.5 mg kg-1, i.p.) or saline at an ambient temperature of 21ºC and rectal temperature monitored for 6 h. Animals were killed 7 d after MDMA and the density of cortical [3H]paroxetine-labelled 5-HT uptake sites determined. Four days of HS produced a significant increase in cortical Hsp70 expression 24 h after the last exposure (Fig. 1a). HS pretreatment did not alter the MDMA-induced hyperthermic response but partially prevented (37%) the MDMA-induced reduction in 5-HT uptake site density 7 d later (Fig 1b).
Figure 1. (a) HS produced an increase in cortical Hsp70 expression 24 h after treatment. Different from control: *P<0.05 (Student’s t-test). Blot shows a representative sample from each group. (b) MDMA-induced reduction in cortical 5-HT uptake site density 7 d later was partially prevented by HS pretreatment. Different from saline: **P<0.01, ***P<0.01. Different from MDMA (12.5 mg kg-1): ΔP<0.05 (Newman-Keul’s test). Data shown as mean ± s.e.mean, n=4-6. This suggests that increased Hsp70 levels may be involved in mediating the HS preconditioning mechanism against MDMA-induced 5-HT damage in Dark Agouti rats.
Dirnagl, U. et al., (2003) TINS 26, 248-254. E.O.S. thanks CAM ( 08.8/0004.1/2003) and PNSD (MSC) and MCYT ( SAF2003-05180) for support. |