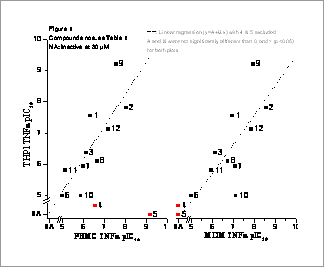
Characterisation of different macrophage cell systems using TNFα production inhibitors With the advent of biological drugs, TNFα antagonism is now a well-validated approach to treat rheumatoid arthritis. In an effort to discover more efficacious and safer molecular targets for TNFα inhibition, a high throughput screen (HTS) was run to identify inhibitors of LPS driven TNFα production in an appropriate macrophage-like cell line, such as PMA pre-treated THP1 cells. To ascertain the suitability of THP1 cells as a surrogate cell system, we used a panel of known blockers of TNFα production (Table 1) to compare PMA pre-treated THP1 cells with peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) and monocyte derived macrophages (MDM) preparations.
Cells were incubated in DMEM and compounds added 30 minutes prior to an addition of an LPS EC80 (10 ng/ml for PBMC/MDM; 1 μg/ml for THP1). TNFα levels in cell supernatants were measured after 4 hours using a FLISA (Miraglia et al., 1999). pIC50 values were determined in 3-9 independent experiments and SEM values were within 10% of the mean. Figure 1 shows correlations between data for each assay. The majority of the inhibitors were of similar potency in all assays, except for the PDE inhibitors, which were active only in the PBMC assay. The THP1 assay was selected for HTS as it detected the majority of known mechanisms of TNFα inhibition as exemplified by the standard compounds.
Baxter et al. (2004) Bioorg. Med. Chem. Letts. 14 (11): 2817-2822. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||