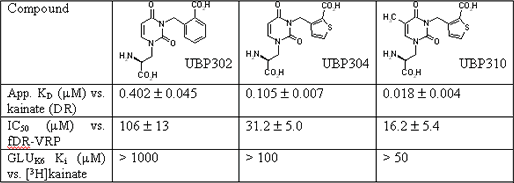
Novel potent gluk5 selective kainate receptor antagonists In recent years we have developed willardiine derivatives with antagonist activity at AMPA and kainate receptors. In this study we describe two new potent and selective willardiine-derived antagonists at GLUK5-containing kainate receptors, UBP304 and UBP310, and compare them to the known antagonist UBP302 (More et al., 2004). Methods were carried out as described previously (More et al., 2004). Briefly, to measure GLUK5-containing kainate receptor activity recordings were made from dorsal roots of P4 Wistar rats of either sex (7-12g). Depolarisations evoked by kainate were measured in the absence and presence of the antagonists. To assess AMPA receptor antagonist activity the ability to depress the fast component of the dorsal root evoked ventral root potential (fDR-VRP) in the hemisected rat spinal cord was measured. The same preparation was used to gauge the selectivity of UBP310 by measuring the depression of responses evoked by NMDA and the group I mGluR agonist DHPG, in the presence of 0.1 μM tetrodotoxin. In radioligand binding studies the ability of antagonists to displace 3Hkainate from HEK293 cells transiently transfected with rat GLUK6 was measured. The ability of UBP304 to inhibit glutamate-induced Ca2+ influx using recombinant human AMPA or kainate receptor subunits stably expressed in HEK293 cells was measured using a fluorometric imaging plate reader. All results are expressed as mean ± s.e.m., n=3. The structures and selected data are shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Structures and pharmacological data (DR = dorsal root). UBP304 inhibited glutamate induced Ca2+ influx in cells expressing human GLUK5, GLUK5/GLUK6 and GLUK5/GLUK2 with Kb values of 0.12 ± 0.03, 0.12 ± 0.01 and 0.18 ± 0.02 μM, respectively. In selectivity studies, UBP310 (10 μM) or UBP304 (50 μM) did not antagonise responses evoked by NMDA or DHPG in the spinal cord. UBP304 (100 μM) had little effect on glutamate induced Ca2+ influx in HEK293 cells expressing human GLUK6, GLUK6/GLUK2 kainate receptor or GLUA1, GLUA2, GLUA3 or GLUA4 AMPA receptor subunits. Thus, UBP304 and UBP310 show high selectivity for the GLUK5 kainate receptor subunit. UBP310 is the most potent GLUK5 kainate receptor antagonist so far described and is likely to be a useful pharmacological tool in physiological studies.
More, J.C.A. et al., (2004) Neuropharmacology , 47, 46-64. |