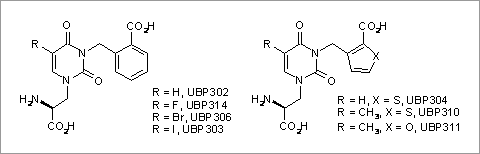
Structure activity relationships for novel willardiine-derived GLUK5 kainate receptor antagonists In recent years we have developed several willardiine derivatives with antagonist activity at AMPA and kainate receptors (More et al., 2004). In this study structure-activity relationships (SARs) for novel willardiine-derived GLUK5-containing kainate receptor antagonists are described. Methods were carried out as described previously (More et al., 2004). Briefly, to measure GLUK5-containing kainate receptor activity recordings were made from dorsal roots of P4 Wistar rats of either sex (7-12 g). Depolarisations evoked by kainate were measured in the absence and presence of the antagonists. To assess AMPA receptor antagonist activity the ability to depress the fast component of the dorsal root evoked ventral root potential (fDR-VRP) in the hemisected rat spinal cord was measured. All results are expressed as mean ± s.e.m., n=3. Structures and data are shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Structures and pharmacological data for willardiine derivatives. None of the compounds tested had potent AMPA receptor antagonist activity. The following conclusions concerning GLU K5 antagonist activity can be made: The rank order of potency for substitution at the 5-position of the uracil ring of UBP302 derivatives is Br>I>F>H. A thiophene ring was preferable to a furan or benzene ring. Addition of a methyl group to the 5-position of the uracil ring of UBP304 to give UBP310 also enhanced antagonist activity at GLUK5-containing kainate receptors. The preference for a thiophene ring indicates that space is tight around the site of interaction of the terminal carboxylate group, while the preference for a methyl group at the 5-position of the uracil ring suggests that there is an interaction with a hydrophobic pocket in the GLUK5 receptor. The lower potency of the furan derivative UBP311 reflects adverse interactions of the electronegative oxygen atom in a hydrophobic environment. The results obtained for UBP302 derivatives indicate that a 5-position substituent as large as bromo is accommodated by the GLUK5 receptor. As a result of this SAR study we have identified UBP310 to be a potent GLUK5 kainate receptor antagonist.
More, J.C.A. et al., (2004) Neuropharmacology , 47, 46-64. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||