Print version
Search Pub Med
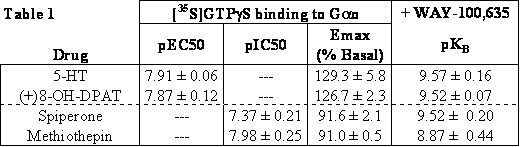
Cloned human 5-HT1A receptors stably expressed in chinese hamster ovary cells show constitutive activity as revealed by inverse agonist properties of spiperone and methiothepin (Newman-Tancredi et al., 1997; McLoughlin et al., 2000). In the present study, we evaluated constitutive activity of native 5-HT1A receptors in membrane preparation from rat (male Sprague Dawley) hippocampus, a tissue enriched in 5-HT1A receptors (Pompeiano et al., 1992). We first demonstrated with antibody capture scintillation proximity assays using Gα protein subtype-specific antibodies that hippocampal 5-HT1A receptors couple to Gαo, and not to Gαs or Gαq/11. Under low sodium (30 mM) conditions, we observed high [35S]GTPγS basal binding to Gαo protein (defined as 100%). In this assay, 5-HT and the prototypic selective 5-HT1A agonist (+)-8-OH-DPAT both stimulated Gαo to a similar extent (Table 1). The effect of a fixed concentration (1 µM) of either agonist was completely inhibited by WAY100,635 (Table 1). Increasing concentrations of WAY100,635 alone were without any effect on Gao activation, suggesting neutral antagonist properties of this drug in these conditions.
On the other hand, spiperone and methiothepin showed inverse agonist properties, reducing basal Gao activation in a concentration-dependent manner (Table 1). The inhibition of Gao activation by maximally effective concentrations of spiperone (10 µM) or methiothepin (1 µM) was reversed by WAY100,635 (Table 1). These data provide the first experimental evidence that 5-HT1A receptors exhibit constitutive activity in native rat brain tissue.
|
|