186P University of Oxford
BPS 75th Anniversary Meeting December 2006 |
The novel ligand [ 125i]-QRFP43 reveals a remarkably discrete distribution of the orphan receptor GPR103 in human adrenal
R.E. Kuc, J.D.Mitchell & A.P. Davenport. Clinical Pharmacology Unit, University of Cambridge, Level 6 Centre for Clinical Investigation, Box 110 Addenbrooke’s Hospital, Cambridge , CB2 2QQ, UK.
The forty-three amino acid peptide, QRFP43, has recently paired with a previously designated ‘orphan’ G-protein-coupled receptor, GPR103 (SP9155/AQ27, Jiang et al., 2003; Fukusumi et al., 2003). Molecular studies suggest the presence of mRNA encoding both peptide and receptor in humans. Our aim was to design a novel radioligand, [ 125I]-QRFP43 and for the first time to characterise the receptor protein and determine its distribution in a range of peripheral human tissues.
An initial autoradiographical screen was carried out using tissues (n=3 individuals) obtained with informed consent, from patients undergoing cardiothoracic surgery (left ventricle, aorta, coronary, radial and internal mammary arteries, saphenous vein and graft and lung), nephrectomy or unilateral adrenalectomy. Detailed autoradiography and saturation analyses were performed on cryostat sections (10μm) of adrenal (Davenport & Kuc, 2005). Following optimisation of binding conditions, sections were pre-incubated for 30min in 50mM NaH2PO4 buffer, pH7.4 containing 100mM NaCl, 5mM MgCl2, 5mM EDTA and 0.1%BSA then incubated with a fixed concentration (0.2nM) for autoradiography or, for saturation studies, increasing concentrations (15pM-4nM) of [ 125I]-QRFP43 (custom synthesis by Amersham Biosciences, GE Healthcare) for 2 h. Unlabelled QRFP43 (10µM) was used to determine non-specific binding within adjacent sections. Sections were washed for 3x5min in 50mM Tris-HCl, dipped in ice-cold de-ionised water, dried and apposed to radiation sensitive film, Biomax-MR with [ 125I]-microscale standards for one week. Densitometric analysis of the autoradiograms was performed (Quantimet 970, Leica) to obtain the amount of specific binding to the discrete regions of the adrenal sections and analysed using the KELL suite of programmes (Biosoft, UK).
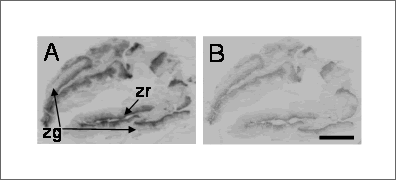
Figure 1. Representative utoradiogram showing:
(A) total [ 125I]-QRFP43 binding to human adrenal
(B) Non-specific binding. Scale bar =5mm.
Tissue profiling revealed a remarkably discrete distribution amongst the human tissues tested with highest densities of specific [ 125I]-QRFP43 binding to human adrenals predominately to the zona reticularis and glomerulosa. Specific binding was below the level for detection in the zona fasciculata of the cortex and medulla. Over the concentration range tested, [ 125I]-QRFP43 binding to zona reticularis was saturable. The ligand bound with high affinity (K D = 1.06 ± 0.7nM, mean ± s.e.mean) with a Bmax of 51.6 ± 5.7fmol mg -1 protein. A one site fit was preferred to a two-site model using the F-test in the Ligand programme and Hill coefficients were close to unity (nH=1.2 ± 0.2).
The discrete localisation of receptors to the cells of the zona reticularis and glomerulosa is intriguing and consistent with the modulation of adrenal function following intravenous administration of the peptide in animals (Fukusumi, S. et al. 2003).
Davenport , A.P. & Kuc, R.E. (2005). In:Methods Mol Biol. 306:93-120, 2005
Fukusumi, S. et al. (2003). J Biol Chem; 278: 46387-46395
Jiang Y et al. (2003). J Biol Chem; 278: 27652-27657
|


