006P Brighton
Winter Meeting December 2008 |
The binding kinetics of a fluorescent agonist at the human adenosine A3 receptor in whole cells
Lauren May, Stephen Briddon, Stephen Hill
University of Nottingham, Nottingham, UK
The synthesis of ABA-X-BY630, a novel N6-aminoalkyl derivative of adenosine which incorporates the BODIPY 1 fluorophore has been described previously (Middleton et al, 2007). This study has investigated the association and dissociation kinetics of ABA-X-BY630 at the adenosine A3 receptors in the absence and presence of an unlabelled antagonist at a single cell level.
CHO cells stably expressing the human adenosine A3 receptor were exposed to HEPES-buffered saline solution (HBSS) containing 100 nM ABA-X-BY630 for approximately 70 seconds after which time cells were washed with HBSS alone or in the presence of 1 μM MRS 1220. A perfusion system with a flow rate of approximately 20 mL.min-1 was used for the addition and removal of ligand. For the duration of the experiment, confocal fluorescence and phase images were obtained at one second intervals using a Zeiss 510 confocal microscope. Each replicate represents the average fluorescence intensity (%) of the plasma membranes of 10 cells.
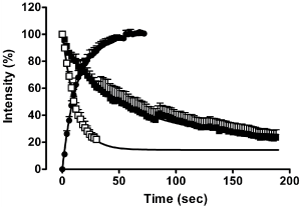
Figure l: ABA-BY630 association (•) and dissociation kinetics in the absence ( ) and presence ( ) and presence ( ) of 1μM MRS 1220. Data points represent the mean ± S.E.M. of 40-70 cells from 4-7 separate experiments. Two second intervals shown for clarity ) of 1μM MRS 1220. Data points represent the mean ± S.E.M. of 40-70 cells from 4-7 separate experiments. Two second intervals shown for clarity
The association of ABA-X-BY630 at the adenosine A3 receptor was monophasic with an association rate constant, kon, of 574700 ± 19000 M-1sec-1 (mean ± S.E.M. n=7). ABA-X-BY630 dissociation was determined under conditions reflecting that of infinite dilution in the absence and presence of the selective adenosine A3 antagonist, MRS 1220. Under both conditions, ABA-X-BY630 dissociation was monophasic, however the dissociation rate in the absence of antagonist (koff = 0.019 ± 0.001 sec-1, mean ± S.E.M., n=4) was significantly slower than that in the presence of 1 μM MRS 1220 (koff = 0.080 ± 0.007 sec-1, mean ± S.E.M., n=4).
In summary, confocal imaging has been used to directly measure, at single cell level, the binding kinetics of the fluorescent adenosine agonist, ABA-X-BY630. In addition, the perfusion system allows for the rapid removal of ligand and as such the comparison of ABA-X-BY630 dissociation in the absence and presence of antagonist. Under infinite dilution conditions, the dissociate rate of ABA-X-BY630 should be unaffected by the presence of a simple competitive antagonist. Therefore the ability of MRS 1220 to enhance the dissociation rate of ABA-X-BY630 suggests that there may be a negatively cooperative interaction occurring between the two ligands.
Middleton, R.J. et al. (2007) J. Med. Chem., 50, 782-793
|


