Rho-A dependent kinase (ROCK) activation occurs during early reperfusion following prolonged ischaemia: effect of ischaemic preconditioning and postconditioning Inhibition of Rho-A dependent kinase (ROCK) activation at reperfusion following myocardial ischaemia limits tissue injury (Hamid et al., 2007). Reactive oxygen species (ROS) may be potent activators of ROCK. Since ischaemic preconditioning (IPC) and postconditioning (IPost) reduce ROS generation at reperfusion, we hypothesised that ROCK activation occurs at early reperfusion via ROS generation, and that this activation is inhibited by both IPC and IPost. The aim was to investigate ROCK activity in ischaemia-reperfusion using phosphorylated ezrin/radixin/moesin (phospho-ERM) as a biomarker. 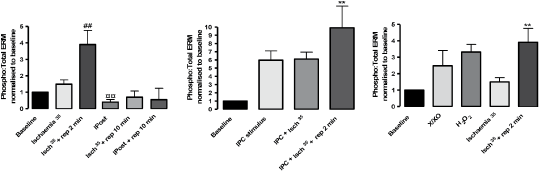
Figure 1. **P<0.01 vs. Baseline; ##P<0.01 vs. Isch35; ¤¤P<0.01 vs. Isch35 + rep 2 min. 1-way ANOVA + Newman-Keuls post hoc; n = 4-8 per group Transient ROCK activation occurred at early reperfusion, an effect mimicked by ROS exposure. IPost inhibited ROCK activity in reperfused myocardium but, paradoxically, IPC induced activation of ROCK. Thus, the putative deleterious role of ROCK activation at reperfusion requires further investigation. |
|

