Searching for histamine H4 receptor ligands among derivatives with N-methylpiperazine amide motif Histamine H4 receptor, the most recently identified histamine receptor, is a promising target for search of new active ingredients of drugs as it is expressed at high levels in mast cells and leucocytes. Studies indicated that modulation of H4 receptor activity provides an opportunity for treating inflammatory and allergic conditions. During the search for histamine H4-receptor ligands, a number of compounds with N-methylpiperazine moiety showed interesting activity, including clozapine analogs1, 2-arylbenzimidazole derivatives2 and, especially, acyl derivatives, JNJ7777120 and VUF 6002, with affinities at H4R in nanomolar range.3 Analysis of active acylic N-methylpiperazine derivatives suggested that N-methylpiperazine with carbonyl linker as well as aromatic fragment are crucial for histamine H4R-antagonistic properties. Basing on this idea, a series of JNJ7777120 analogs was designed and synthesized (Fig.1). The compounds belonged to four following groups: (1) benzoic-, (2) coumarinic-, (3) benzothiophene-2-carboxylic-, and (4) 3,5-dihydroimidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-2-carboxylic acid derivatives. The compounds were obtained within 1-4-step syntheses including different cyclic condensations (group 2-4), ester hydrolysis (group 4), conversion into acid chlorides (group 2 and 4) and N-acylation processes. 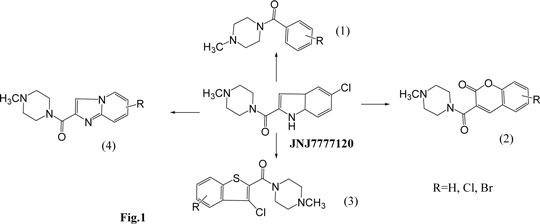
The obtained compounds showed moderate or low affinity for H4R receptor. The most promising one was 3,5-dichlorobenzo[b]thiophene-2-carboxylic acid derivative. SAR-study indicated that decrease of activity, comparing to properties of lead JNJ7777120, seems to be related to lack of -NH- at heterocyclic part of the new compounds.
1R.A. Smith et al., J. Med. Chem., 2006, 49, 4512-4516. The authors acknowledge the support of ESF COST Action BM0806 ‘Recent advances in histamine receptor H4R research’, financed by EU-FP7. Partly supported by the Ministry of Scientific Research and Information Technology, Poland grant No. DAAD/55/2007.
|
|

