Membrane phospholipid (PL) binding to M-type potassium channel subunit Kv7.2 C-terminal fusion proteins in vitro. Like many other ion channels, Kv7 K+ channels require membrane phospholipids (especially phosphatidylinositol-4.5-bisphosphate, PI(4,5)P2) for normal function. We have previously reported the binding of PLs to a Kv7.1 C-terminal (Q1C)/ maltose binding protein (MBP) fusion protein using a protein-phospholipid overlay assay (Thomas et al, 2011). Using similar techniques we have now assayed PL-binding to the C-terminus of the homologous Kv7.2 channel (Q2C). The full-length C-terminus of Kv7.2 (Kv7.2C; amino acids 318 to 845) was cloned into the pmalc2x vector (NEB) to create a C-terminal fusion with maltose-binding protein (MBP). MBP-Q2C was expressed and purified as shown in Fig 1A. The protein-lipid overlay assay (Fig 1B) revealed a broad spectrum of PL binding, like MBP-Q1C. Mean spot intensities (n = 3) for MBP-Q2C (MBP-Q1C in brackets; Thomas et al, 2011) were: PI 7.71 (0); PI(3)P 47.3 (29.9); PI(4)P 38.8 (36.2); PI(5)P 51.1 (57.4); PI(3,4)P2 12.3 (6.5); PI(3,5)P2 21.9 (36.5); PI(4,5)P2 46.1 (15.4); PI(3,4,5)P3 14.3 (39.7). Q1C and Q2C intensities were not significantly different (P>0.05, t-test). We conclude that Kv7 C-termini bind a range of phosphoinositides. Support 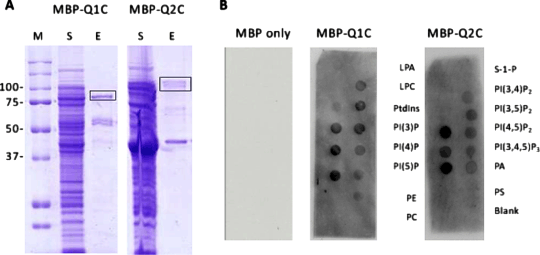
Figure 1. Purification and PL-binding of maltose binding protein– Kv7 C-terminal fusion proteins (MBP-Q1C and MBP-Q2C). A. Coomassie stained SDS-PAGE gels showing the induced expression in bacteria and recovery after purification of soluble MBP-QC fusions. S, soluble fraction; E, eluted protein (10 mM maltose, 2 g protein loaded). B. Protein – lipid overlay assays. P, phosphatidylinositol; PI(n)P, phosphatidylinositol(n) phosphate; PI(n)P2, phosphatidylinositol(n) bisphosphate; PI(n)P3, phosphatidylinositol(n) trisphosphate; PA, phosphatidic acid; PS, phosphatidylserine; PC, phosphatidylcholine; PE,phosphatidylethanolamine; LPA, lysophosphatidic acid; LPC, lysophosphatidylcholine; S-1-P,sphingosine-1-phosphate.
Thomas et al, 2011: J Biol Chem. 286:2088-2100.
|
|

