Neuroprotective effect of senna extract in rat model of Parkinson’s disease The ability of Cassia angustifolia (senna) extract in rat model of Parkinson’s disease has been assessed in this study. In this experimental study, 60 male Wistar rats (240-260 g) divided into six groups (control, sham, lesion, 3 treatment group with oral administration of 3 concentrations of senna extract) were used. Oral administration of the extract with 25, 50 or 100 mg/kg/daily dose was started one week before the model creation procedure and continued during the whole treatment period. The laboratory model of Parkinson’s disease in rats was performed by injecting 2.5 microlitre saline solution 0.9 % containing 8 micrograms 6-hydroxy dopamine (6-OHDA) and 0.2 % ascorbic acid in striatum. Also in sham group, the same volume solution saline-ascorbic was injected. Behavioral assessment before and two weeks after creating the model was performed using apomorphine-induced rotational behavior in rats with unilateral striatum lesions. Challenge with apomorphine (2.5 mg/kg IP) elicited rotational behavior. Also, at the end of second month of treatment, histologic studies were performed and the cells were then quantified by counting the average number of cells in six serial sections through the substantia nigra of each animal. Cell counts were obtained under blind conditions. Results are expressed as means ± S.E.M. Data were subjected to one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey–Kramer post hoc analysis. Significance was ascertained at p<0.05. Behavioral assessment of treatments groups (Fig. 1) showed a considerable recovery compared with lesion group )p<0.001(. Cell count assessment (Fig. 2) showed that the number of neural cells in the treatment group was significantly different from other experimental groups. In conclusion, senna extract can have an effective role in the treatment of Parkinson\'s disease. 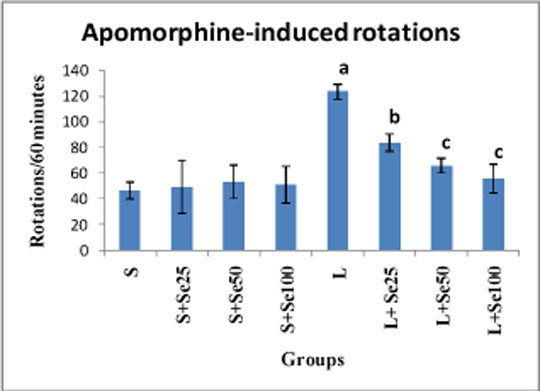
Fig 1. Effect of Senna extract on apomorphine-induced rotations in sham-operated (S) and 6-OHDAlesioned (L) rats. Rats were pre-treated with either vehicle (S=sham, L=lesion) or various concentrations of the extract (25, 50 or 100 mg/kg/day for 7 days, followed by unilateral intrastriatal injection of either vehicle (S=sham groups) or 6-OHDA (L=lesion groups). Values are expressed as means ±S.E.M. a: p <0.005 vs. S; b: p <0.05 vs. L; c: p <0.005 vs. L. 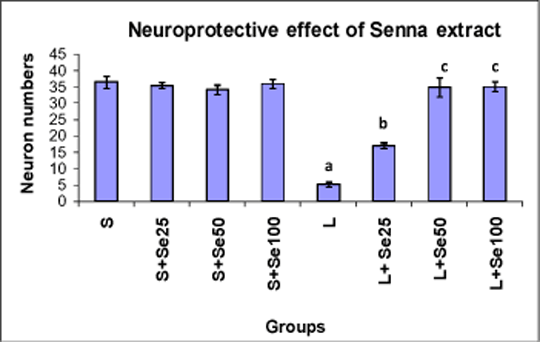
Fig 2. Effect of Senna extract on neuron number in sham-operated (S) and 6-OHDAlesioned (L) rats. Rats were pre-treated with either vehicle (S=sham, L=lesion) or various concentrations of the extract (25, 50 or 100 mg/kg/day for 7 days, followed by unilateral intrastriatal injection of either vehicle (S=sham groups) or 6-OHDA (L=lesion groups). Values are expressed as means ±S.E.M. a: p <0.001 vs. S; b: p <0.01 vs. L; c: p <0.001 vs. L. Keywords: Senna, Neuroprotective, Parkinson\'s disease, Rat.
|

