Print version
Search Pub Med
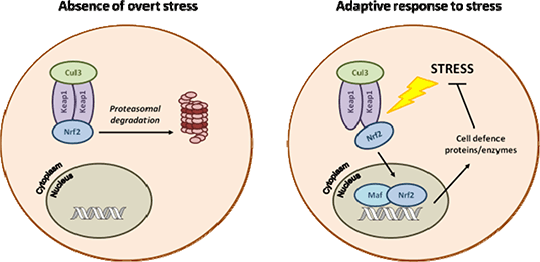
Proteomic analysis reveals vital role of the transcription factor Nrf2 in the regulation of cell defence processes in the mouse kidney Drug-induced acute kidney injury is a significant clinical problem, and accounts for the cessation of development of many promising drug candidates. Increasing evidence supports a vital role for the transcription factor Nrf2 in protection of the kidney against a number of diseases and toxicities (1; Fig. 1), and the pharmacological induction of Nrf2 by CDDO-Me (methyl-2-cyano 3,12-dioxooleano-1,9-dien-28-oate, bardoxolone methyl) has shown promise for the clinical management of such pathologies. To provide a comprehensive analysis of the biological processes that are regulated by Nrf2 in the kidney, and to explain the means by which Nrf2 affords protection against a number of nephrotoxins, we have undertaken an iTRAQ-based proteomic analysis of whole kidney homogenates from wild type (Nrf2+/+) and transgenic Nrf2 knockout (Nrf2-/-) mice, both basally and following treatment with 3 mg/kg CDDO-Me (I.P. in DMSO) for 24 h (n=6 animals per group). 
Fig. 1 > Overview of the Nrf2 pathway A total of 3684 unique proteins were quantified over all samples and searched against a reverse decoy database. Only proteins identified within a 1 % global false detection rate were included in subsequent analyses. Of these, 136 proteins were altered between the Nrf2+/+ and Nrf2-/- vehicle control groups (P<0.05, unpaired t-test), including substantial reductions in the expression of the cell defence proteins glutathione S-transferase Mu 1 (relative expression versus pooled control sample 0.18 ± 0.09 in Nrf2-/-, 2.08 ± 0.40 in Nrf2+/+, 11.5-fold change), catalase (0.63 ± 0.16 in Nrf2-/-, 2.70 ± 0.71 in Nrf2+/+, 4.3-fold change) and NAD(P)H dehydrogenase [quinone] 1 (0.35 ± 0.09 in Nrf2-/-, 1.25 ± 0.25 in Nrf2+/+, 3.6-fold change). Whilst a single dose of CDDO-Me was sufficient to induce the expression of NAD(P)H dehydrogenase [quinone] 1 in the kidneys of Nrf2+/+ mice (1.70 ± 0.31 in CDDO-Me, 1.25 ± 0.25 in vehicle, 1.4-fold change), none of the 17 other proteins that were significantly altered (P<0.05, unpaired t-test) by CDDO-Me in Nrf2+/+ animals were found to be regulated by Nrf2 at the basal level. These data, supported by Metacore pathway analysis and quantitation of mRNA, highlight the role of Nrf2 as a key regulator of cellular defence processes in the kidney, and provide a rationale for our ongoing investigations into the capacity of Nrf2 to protect against drug-induced nephrotoxicity. Moreover, these data justify further evaluation of the biological effects of CDDO-Me and other Nrf2 inducers in the kidney, in order to determine the risk:benefit of this compound class as potential modulators of kidney disease. 1. Shelton LM, Park BK, Copple IM (2013) Kidney Int. [Epub ahead of print].
|