Print version
Search Pub Med
Use of a mathematical formula in association with the Evan’s Blue dye technique to quantify oedema formation in skin Vascular permeability is enhanced in post-capillary venules during an inflammatory response, resulting in plasma extravasation which is mediated by an array of inflammatory mediators. Previously, the quantitative 125I-albumin technique was used to assess oedema formation in vivo (Williams & Morley, 1974) but access to 125I-albumin is now limited. Consequently, the traditional method of Evan’s Blue dye accumulation remains popular for skin bioassays (Edlund & Juhlin, 1955; Sawyer et al., 2011). In this study, we have used a half-ellipsoid model for volumetric calculation to assess cutaneous oedema formation in association with the use of Evan’s Blue dye to provide a novel approach in analysing oedema formation. CD1 mice (25-40g, mixed gender) were anaesthetised by i.p. urethane (7µl/g) and the dorsal skin was shaved. The skin assay was performed according to Sawyer et al. (2011) with 6 sites of interest (50µl i.d. per site): uninjected, sham injection, Tyrode’s solution (vehicle control), substance P (SP; 300pmol), calcitonin gene related peptide (CGRP; 10pmol), and CGRP & SP co-treatment. Oedema formation was analysed qualitatively by colour intensity of skin (score 0-5) and quantitatively by oedema diameter and volume. Assuming oedema formation was ellipsoidal, the volume around the injection site was calculated using the following formula: 
The results regarding the mediator effects (described previously by Brain and Williams, 1985) are summarised in table 1.
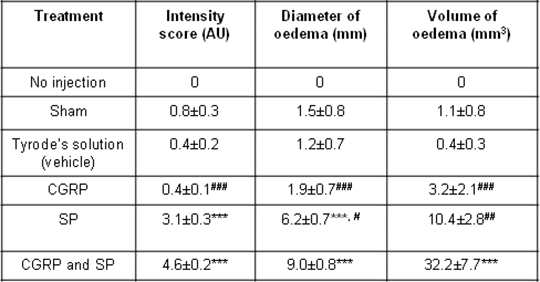
Table 1: Summary of the oedema attributes in response to i.d. injections of the treatment. Data illustrated as mean ± S.E.M. and statistical analysis performed by Kruskal-Wallis followed with the Dunn’s post hoc test for intensity scores and one way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test for the oedema mean diameter and volume, where ***p<0.001 illustrates comparison to Tyrode’s solution, and #p<0.05, ##p<0.01, ###p<0.001 in comparison to CGRP and SP co-treatment. 
In conclusion, the use of a half-ellipsoid model enhances the analytical measurements of Evan’s Blue responses following local oedema formation by enabling skin volume assessment, without the need to quantify Evan’s blue dye following extraction from the skin. Brain SD & Williams TJ, Br J Pharmacol 86: 855-860, 1985 Edlund T, Juhlin L, Acta Pharmacol et Toxicol 11: 187-192, 1955 Sawyer et al, PloS One 6: e14671, 2011 Williams TJ & Morley J, Br J Exp Path 55: 1-12, 1974 |