Print version
Search Pub Med
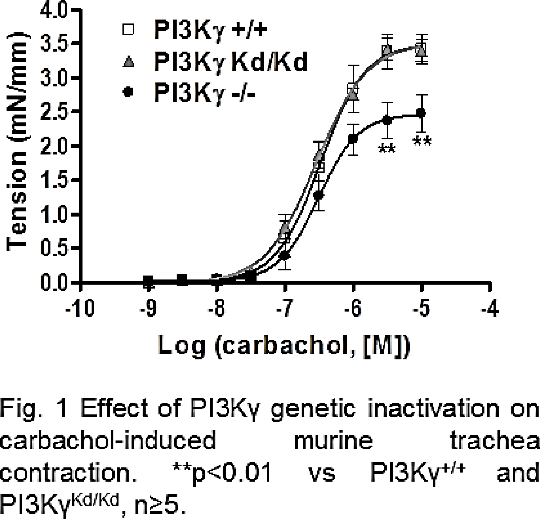
PI3Kγ modulates airway smooth muscle contraction, through the regulation of PDE4B enzymatic activity In cardiomyocytes, PI3Kγ acts as a negative regulator of β2-ARs signalling, by increasing phosphodiesterases (PDEs) enzymatic activity, allowing the fine tuning of cAMP levels in the heart (1, 2). Given this notion, the aim of the study was to investigate whether PI3Kγ might play a role also in the regulation of airway smooth muscle cells (ASMC) contraction and to examine its interaction with PDE type 4. METHODS. Tracheal segments (2-3mm) obtained from PI3Kγ+/+, PI3KγKd/Kd (kinase dead) and PI3Kγ-/- adult male C57BL/6J mice were mounted on a wire myograph and treated with carbachol (10-9 M – 10-5 M). The contractile response has been expressed as mean isometric tension. ASMC were cultured from explants of PI3Kγ+/+, PI3KγKd/Kd and PI3Kγ-/- mouse tracheas. Whole mouse trachea (WMT) and ASMC lysates were used for PDE4B immunoprecipitation, followed by the measurement of PDE activity using [H]3cAMP. Carbachol-induced contraction was attenuated in PI3Kγ-/- tracheal rings compared to PI3Kγ+/+ and PI3KγKd/Kd. In particular, we measured a reduction in maximal tension, while we didn’t observe differences in terms of potency between the three groups (Fig. 1). We observed a 40-50% reduction of PDE4B activity in PI3Kγ-/- WMT and ASMC compared to PI3Kγ+/+ and PI3KγKd/Kd suggesting that the reduced contraction in PI3Kγ-/- tracheas could be due to a reduction in cAMP hydrolysis by PDEs (Table1).  
Table 1 PDE4B activity (cpm/ip * 104, n≥4) in WMT and in ASMC from PI3Ky+/+, PI3Kykd/kd and PI3Ky-/- mice. **p<0,01 vs PI3Ky+/+ and PI3Kykd/kd; ##p<0,01 vs PI3Ky+/+ and PI3Kykd/kd. In summary, this data indicates that PI3Kγ is able to enhance PDE4B activity in ASMC. This molecular interaction plays a role in modulating intracellular levels of cAMP and ASMC contraction. (1) Perino A et al, Mol Cell 42:84, 2011 (2) Ghigo A et al, Circ 126:2073, 2012
|