Print version
Search Pub Med
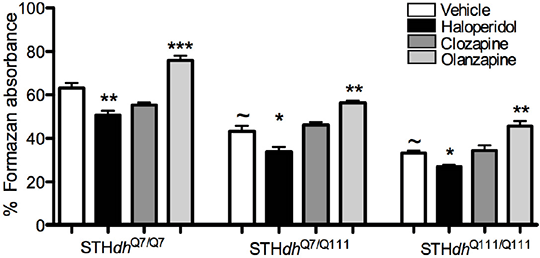
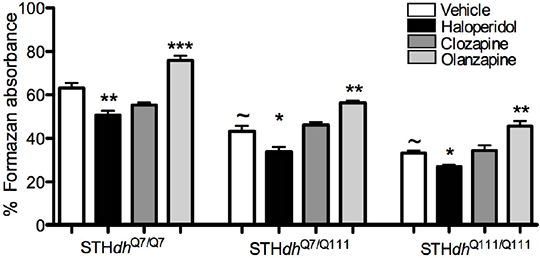
Olanzapine improves mitochondrial function in an in vitro model of Huntington’ s disease Huntington’s disease (HD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by motor disturbances, psychiatric dysfunctions, and cognitive disabilities. HD is caused by the expression of the gene encoding mutant huntingtin (mHtt), which causes transcriptional dysregulation of a subset of genes (reviewed in 1). Antipsychotic drugs are used for HD patients to improve motor impairments and to alleviate psychotic symptoms (2). Typical and atypical antipsychotic drugs have been shown to have different clinical, biochemical and behavioural profiles (3). The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of haloperidol, clozapine and olanzapine treatment on the survival rate and metabolic activity using a striatal cell model of HD. In this study, the STHdhQ 7/Q7 cells, that express physiological levels of the wild-type Htt, and STHdhQ 7/Q111 and STHdhQ 111/Q111 cells, that express one or two copies of mHtt, respectively, were used. Cells were treated with 1.0 µg/µl haloperidol, clozapine, olanzapine or vehicle for 20 hours. Cell viability was measured using ethidium homodimer staining (Eth-D1). Cells with compromised membranes take up EthD-1. Then intercalate with DNA and fluoresce red. Mitochondrial activity was measured using the XTT tetrazolium assay. Mitochondrial dehydrogenases convert tetrazolium salt into formazan. Cell viability and metabolic activity were lower in mHtt-expressing cells compared to STHdhQ 7/Q7 cells (Fig. 1, 2). Olanzapine treatment increased the cell viability and the metabolic activity of STHdhQ 7/Q7, STHdhQ 7/Q111 and STHdhQ 111/Q111 cells compared to vehicle treatment (Fig. 1, 2). In contrast, haloperidol treatment decreased metabolic activity in the three cell lines without affecting cell viability (Fig. 1, 2). Clozapine treatment did not alter the cell viability or the metabolic activity in the three cell lines (Fig. 1, 2). We are currently examining whether the increase in the metabolic activities by olanzapine is accompanied with an increase in ATP production. We are also examining the effect of antipsychotic drug treatment on PGC1α mRNA expression. Our results demonstrate that antipsychotic drugs have differential metabolic effects on striatal cells. These data suggest that olanzapine may restore cellular metabolism observed in HD. 
Fig. 1 Effect of antipsychotic drugs on cell viability, ~ P< 0.001 compared to STHdhQ7/Q7; ** P < 0.01 compared to vehicle within genotype. 
Fig. 2 Effect of antipsychotic drugs on mitochondrial activity, *** P < 0.001 compared to STHdhQ7/Q7; *** P < 0.001; ** P < 0.01; * P < 0.05 compared to vehicle within genotype (1) Zuccato C et al, Physiol Rev 905-981, 2010 (2) Pidgeon C & Rickards H, Behav Neurol 245-253, 2013 (3) Heiser P et al, J Psychopharmacol 851-856, 2007
|