Print version
Search Pub Med
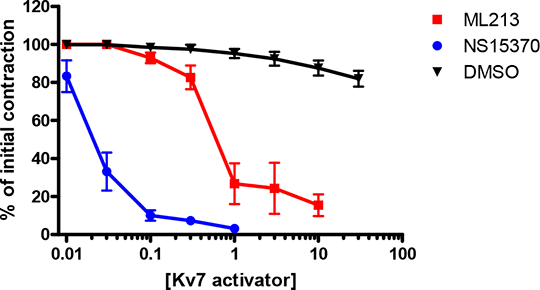
Novel Kv7 activators are potent vasorelaxants. Five members of the KCNQ gene family have been identified (KCNQ1 – 5) that encode channels Kv7.1 – Kv7.5. In vascular smooth muscle, Kv7.4 and Kv7.5 predominate and contribute to vascular reactivity and Kv7 activators reduce vascular tone in rodents and humans effectively (Jepps et al. 2013). This study compared the effectiveness of four established activators of Kv7.2-7.5 (S-1, retigabine, BMS-204352 and ICA-27243) and two novel agents (ML213 and NS15370) at relaxing various rat blood vessels, in a wire myograph under isometric conditions. All the Kv7 activators tested relaxed precontracted segments of thoracic aorta, renal artery and mesenteric artery, in a linopirdine-sensitive manner, with differing efficacies. In each vessel studied, NS15370 and ML213 were the most potent at causing a vasorelaxation, with EC50’s of 0.026 µM and 0.74 µM in the rat mesenteric artery (Figure 1). In isolated rat mesenteric artery cells, ML213 (10 µM) increased the outward potassium current by 23 ± 5 % at 0 mV (n=4). NS15370 (1 µM) also significantly increased the maximal current amplitude and caused leftward shifts in the V½ of activation. A tryptophan residue in the S5 pore domain is known to be crucial for the binding of retigabine, S-1 and BMS-204352, however the binding site for ML213 and NS15370 is unknown. Therefore, electrophysiology experiments were performed on HEK cells overexpressing KCNQ4 or a KCNQ4 mutant with the crucial tryptophan-242 residue changed to a leucine. In the HEK cells overexpressing KCNQ4, NS15370 (1 µM) and ML213 (10 µM) caused leftward shifts in the V½ of activation by -39.8 ± 1.7 mV and -33.0 ± 3.8 mV, respectively. However, in cells overexpressing the mutant KCNQ4, NS15370 and ML213 had no effect (V½ shifts of -0.6 ± 0.9 mV and 2.8 ± 4.6mV, respectively). This study shows that the newly identified Kv7.2-7.5 activators ML213 and NS15370 (Yu et al. 2011; Dalby-Brown et al. 2013) are potent vasorelaxants in a range of blood vessels. These potent Kv7 activators have been developed with anti-epileptic and anti-psychotic treatments in mind; however this study suggests that these new Kv7 activators will effectively alter vascular reactivity and therefore could influence blood pressure control. 
Figure 1: Concentration-effect curves for ML-213 and NS15370 compared to the vehicle control (DMSO) in the rat mesenteric artery, 1: Jepps T.A. et al. Br. J. Pharmacol. 168:19; 2013 2: Dalby-Brown W. et al. Eur J Pharmacol. 709:52; 2013 3: Yu H. et al. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2:572; 2011
|