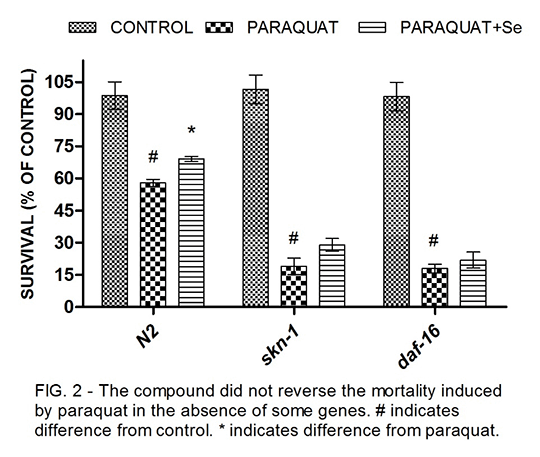
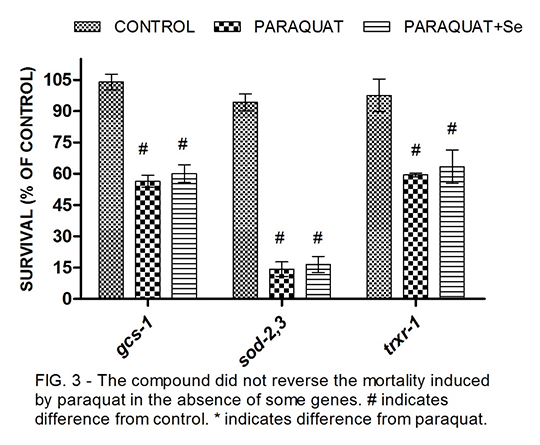
Involment of daf-16, skn-1 and trxr-1 genes in the stress resistance produced by 4-phenylseleno-7-chloroquinoline exposure in Caenorhabditis elegans Alternative in vivo models such as Caenorhabditis elegans have been demonstrated to be an useful tool in Pharmacology, especially for the screening of new drugs. Organoselenium compounds have being extensively studied because of their antioxidant activities, however the molecular mechanisms are still poorly understood and hence, few of the go to clinical trials, sch as ebselen. This study aimed to evaluate the mechanisms of the stress resistance provided by 4-phenylseleno-7-chloroquinoline in C. elegans against paraquat, a well known prooxidant. The N2 (wild type) and knockout strains daf-16, skn-1, sod-2 and 3, gcs-1 and trxr-1 worms were exposed to the organoselenium compound at concentrations that ranged from 1 to 1000µM. To inflict cellular damage, paraquat was used at 500µM and survival was assessed 24hs post-exposure. First of all, we determined the lethal doses 50% (LD50) for the selenoquinoline in the different strains (Fig 1). Hence, we decided to use the concentration of 10 µM against paraquat-induced toxicity. We observed that the compound reduced the mortality-induced by paraquat in about 20%. This effect was completely lost in the absence of the homologues to the human FOXO and NRF2 transcription factors DAF-16 and SKN-1 (Fig. 2). These transcription factors can induce the transcription of protective genes as superoxide dismutase (SOD-2 and SOD-3) and γ-glutamyl cysteine synthetase (GCS-1). In agreement, the same loss of effect was observed in the absence of sod-2,3 and gcs-1. Similarly, the selenoquinoline had no effect in the mutant for thioredoxin reductase 1 (trxr-1) (Fig 3). The selenoquinoline is capable of reverting the mortality in a daf-16, skn-1 and trxr-1 dependent way, indicating that these proteins mediate the antioxidant effect of the selenoquinolines and may be specific targets for next studies.
|