The NK1 receptor antagonist prevents the cyclophosphamide-induced cystitis-related bladder pain and upregulation of cystathionine-γ -lyase, an H2S-generating enzyme, in mice Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) generated by cystathionine-γ-lyase (CSE) participates in somatic or visceral pain processing by enhancing the activity of Cav3.2 T-type Ca2+ channels. We have shown that, in the mouse with cyclophosphamide (CPA)-induced cystitis, a disease model of interstitial cystitis, the bladder pain and inflammation are attenuated by pharmacological and/or genetic inhibition of CSE or Cav3.2, and the protein levels of CSE are upregulated in the bladder tissue (1). To test possible involvement of substance P (SP) in interstitial cystitis, in the present study, we examined the effect of a tachykinin NK1 receptor antagonist on the CPA-induced cystitis/bladder pain and upregulation of CSE in mice. CPA at 300 mg/kg was administered i.p to adult female ddY mice. Bladder pain-like nociceptive behaviour was observed from 3.5 to 4 h after CPA treatment, and referred hyperalgesia was then evaluated by the von Frey test. Thereafter, the bladder was removed, weighed for evaluation of bladder oedema, and used for Western blot analysis of CSE protein. CP-96,345 (CP), an NK1 antagonist, at 5 mg/kg was administered i.p. 30 min before CPA. CP-96,345 (CP) prevented the CPA-induced nociceptive behaviour (Fig.1a), referred hyperalgesia (Fig.1b) and increases in bladder weight (Fig.1c). The CPA-induced upregulation of CSE protein in the bladder tissue was also abolished by CP (Fig.1d). 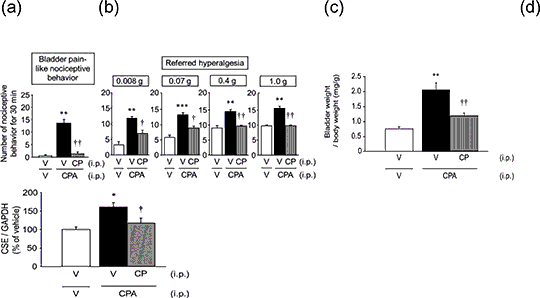 Fig.1 Effect of CP-96,345 (CP), an NK1 receptor antagonist, on the bladder pain-like nociceptive behaviour (a), referred hyperalgesia (b), increases in the bladder weight (c). Data show the mean with S.E.M. for 5-8 mice and upregulation of bladder CSE protein (d) in mice with CPA-induced cystitis. Data show the mean with S.E.M. for 6-11 mice In summary, the NK1 receptor antagonist prevents CPA-induced cystitis/bladder pain and upregulation of CSE in mice, suggesting the involvement of the SP/NK1 pathway in the development of interstitial cystitis-like symptoms including bladder pain, possibly as an upstream signal of the CSE/H2S/Cav3.2 pathway. (1) Matsunami M, Kawabata A et al. (2012) Br J Pharmacol 167: 917-927.
|

