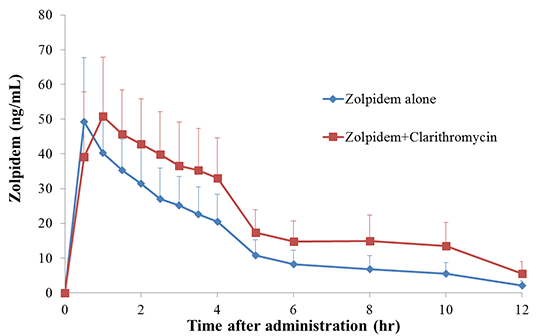
Effects of Clarithromycin on the Pharmacokinetics of Zolpidem Zolpidem, an imidazopyridine derivate, is widely prescribed for the short-term treatment of insomnia. Zolpidem is extensively metabolized to three inactive metabolites by CYP3A4, and to a lesser extent CYP2C9, CYP2C19 and CYP2C1A2. However, there is no report on the drug-drug interaction between zolpidem and clarithromycin, a strong inhibitor of CYP3A4. Our objective was to evaluate a possible pharmacokinetic interaction between zolpidem and clarithromycin, an inhibitor of CYP3A4, in twenty-seven healthy Korean volunteers. The study consisted of two periods: Period 1 (control phase), when each volunteer received a single dose of 5 mg zolpidem and Period 2 (clarithromycin phase), when each volunteer received a single dose of 5 mg zolpidem and 500 mg clarithromycin. Between the two periods, the subjects were treated for 5 days with a dose of 500 mg ciprofloxacin twice a day. Plasma concentrations of zolpidem were determined during a 12-hour period following drug administration. Pharmacokinetic parameters of zolpidem administered in each treatment period were calculated using non-compartmental analysis and the data from two periods were compared to determine statistically significant differences. In the two periods of treatments, the Cmax were 51.4±14.6 ng/ml (zolpidem alone) and 55.6±15.2 ng/ml (zolpidem after pre-treatment with clarithromycin. The total areas under the curve (AUCinf) were 185.1±64.0 and 297.5±107.0 ng h/ml, respectively. Apparent oral clearance (CL/F) of zolpidem was 35.5% lower (0.031±0.014 L/hr vs 0.020±0.013 L/hr) in the clarithromycin phase compared to the control phase (P<0.001). tmax and t1/2 of zolpidem were significantly increased in the clarithromycin phase (0.6±0.2 hr and 2.6±0.6 hr, respectively) than those (1.2±0.8 hr and 3.4±1.0 hr, respectively) in the control phase (P<0.001). These results showed that coadministration of clarithromycin caused an increase in the plasma exposure of zolpidem. This magnitude of effect is likely to be clinically significant. Figure 1. Time-concentration profile of zolpidem after a single dose of 5 mg zolpidem.
|