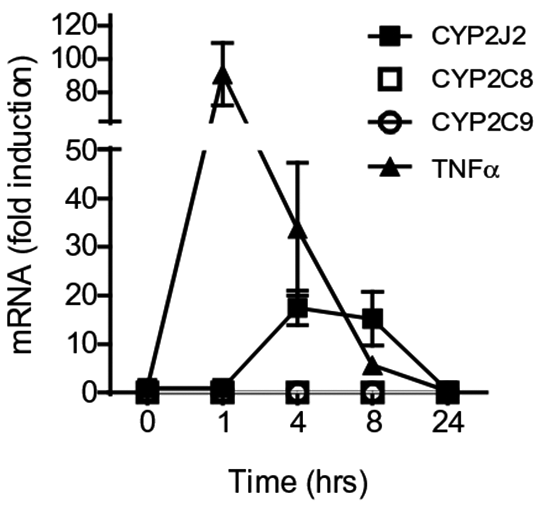
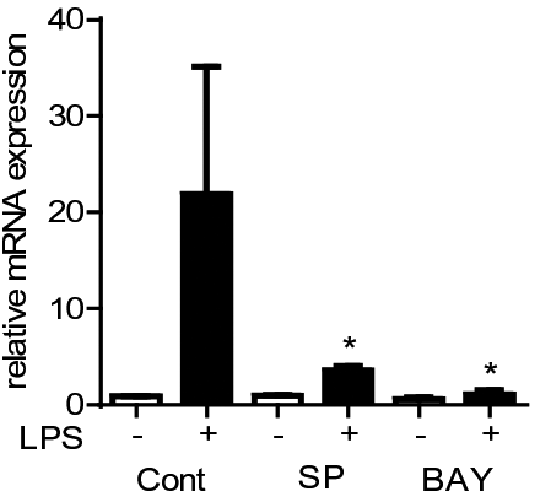
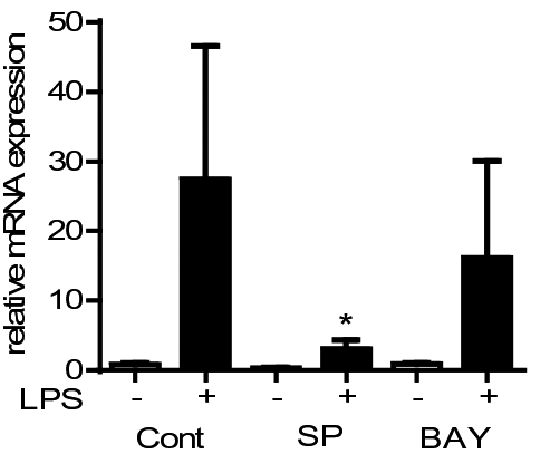
Lipopolysaccharide- induced CYP2J2 in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells requires AP-1 and NFκ B activation Epoxygenases are CYP450 enzymes that convert fatty acids into epoxy-oxylipins e.g. arachidonic acid in to epoxy-eicosatrienoic acids (EETs) (1). In humans the CYP450 family contains 57 genes, however, CYP2J2 and CYP2C family members (CYP2C8, 2C9) are considered the major epoxygenase enzymes (1). We have recently shown epoxygenases are anti-inflammatory in human monocytes and macrophages (2). We also identified CYP2J2 is a TLR-4 inducible CYP. The mechanism by which TLR-4 activation induces CYP2J2 is not known. Leukocytes cones were obtained from the NHS Blood bank. Primary human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated by density centrifugation and cultured in RPMI media supplemented with FCS (10%) and antibiotics (1%) (2). PBMCs were either left unstimulated or stimulated with the TLR4 agonist LPS (10ng/ml; 0-24h) in the presence or absence or inhibitors of inhibition of NF-kB (BAY-11-7082 10μM) or AP-1 (SP600125 10μM) and mRNA levels for CYP2J2, CYP2C8 and CYP2C9, TNFα, and GAPDH quantified by qRT-PCR. CYP2J2 was induced with slow kinetics by LPS in PBMCs compared to TNFα (Figure 1). In contrast, CYP2C8 and CYP2C9 mRNA were not detected at any time-point. LPS (10ng/ml; 4h)-induced CYP2J2 was significantly attenuated by inhibition of NF-kB (BAY-11-7082;10μM) or AP-1 (SP600125 10μM); control 0.01% DMSO (Figure 2). In contrast, TNFα induction by LPS (10ng/ml; 4h) was inhibited by SP600125, but not BAY11-7082 (Figure 3). Data represents n=3 independent experiments from 3 separate donors; * indicates p<0.05; one-way ANOVA.
Figure 1
Figure 2
Figure 3 TLR-4-induced CYP2J2 expression is in primary human PBMCs is dependent on NF-κB and AP-1 activation. The kinetics of CYP2J2 induction suggest, that unlike TNFα, CYP2J2 is not a primary response gene, and since it requires both AP-1 and NFkB activation, but may dependent on the release of additional mediators. (1) Bishop-Bailey D et al., (2014) Annu Rev Nutr. 34: 261-79. (2) Bystrom J et al., (2013) PLoS One. 8: e75107
|