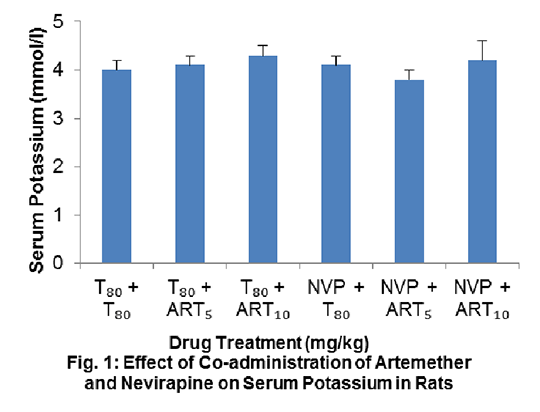
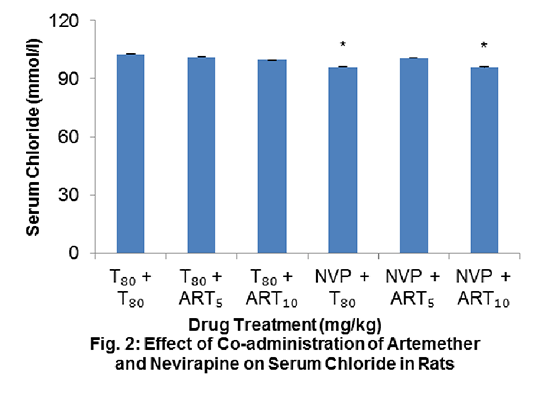
Study on the Effect of Co-administration of Artemether and Nevirapine on Serum Electrolytes in Wistar Rats Artemether (ART) and nevirapine (NVP) are drugs used in the treatment and management of malaria and HIV respectively. There is a possibility for an HIV patient to be on antiretroviral drugs and anti-malarial drugs concurrently, but the safety of such combination therapy is of great concern especially when there is a chance of drug-drug interaction. The objective of this study was to investigate the status of serum electrolyte following co-administration of ART and NVP in Wistar rats. Experiments were carried out according to international ethical standards regarding the handling and use of laboratory animals (1). Rats were divided into 6 groups of 6 per group. Groups 4, 5 and 6 received 30 mg/kg NVP daily for 21 days. From days 15 to 21, groups 2 and 5 received 5 mg/kg ART (ART5) while groups 3 and 6 received 10 mg/kg ART (ART10). All other animals received the vehicle (3% v/v Tween 80 (T80)), up to day 21. All drugs were administered via the intraperitoneal route. On day 22, animals were sacrificed and sera obtained. The levels of Na+, K+, Ca2+, Cl- and HCO3 - were determined using an enzyme selectra XL machine. Data were analysed using ANOVA, followed by Dunnett’s post hoc test and expressed as mean ± standard error of the mean. The level of significance was set at P<0.05. There was no statistically significant difference (p>0.05) in the serum electrolytes (Na+, K+, Ca2+ and HCO3 -) in the experimental groups compared with the control group (Fig. 1); although, the level of Cl- decreased significantly (P<0.05) in NVP + T80 and NVP + ART10 administered groups when compared with the control (96.2±0.5 versus 102.8±0.3) and (96.0±1.5 versus 102.8±0.3) respectively (Fig. 2).
Findings from this study showed no alteration in serum electrolyte levels in Wistar rats co-administered with ART and NVP; although a slight difference in Cl- in NVP + T80 and NVP + ART10 administered groups was observed but this is unlikely to be of concern in the clinical setting. (1) UND/World Bank/WHO (2001). Good Laboratory Practice Training Manual for the Trainee, Pp. 3-19. |