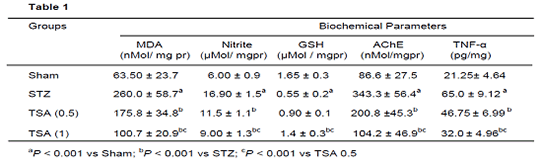
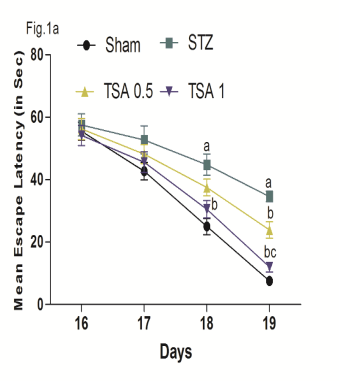
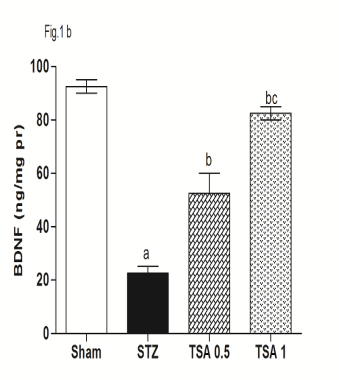
Neuroprotective Effects of HDAC Inhibitor, Trichostatin A, In Intracerebroventricular Streptozotocin Induced Cognitive Deficits In Rats Recent studies have highlighted the pathological role of histone deacetylases (HDACs) in cognitive impairment. The present study was undertaken to determine the therapeutic potential of HDAC inhibitor, Trichostatin A (TSA) in Intracerebroventricular-Streptozotocin (ICV-STZ) induced sporadic Alzheimer's disease. Male Wistar rats (200-250g) were injected with STZ twice (3 mg/kg, ICV) on alternate days (day 1 and 3) using following coordinates: 0.8 mm posterior to bregma; 1.5 mm lateral to sagittal suture; 3.6 mm ventral from the surface of the brain [1]. The ICV-STZ treated rats received either vehicle (0.5% DMSO in saline) or TSA (0.5 and 1mg/kg, i.p.) for a period of 21 days. The results are expressed as mean ± S.D. (n=10). The data was analyzed by One-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's post hoc tests or by Two way ANOVA followed by bonferroni post hoc test, using statistical GraphPad Prism software. P < 0.05 was set to be statistically significant. The ICV-STZ administration results in significant memory impairment, reduced level of brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), the increased oxidative-nitrosative stress, acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity and neuro-inflammation. Using behavioural tests, we observed that TSA treatment dose dependently improved the spatial learning and memory impairments (morris water maze)(Fig.1a, P<0.05). TSA treatment significantly attenuates the oxido-nitrosativeative stress markers, AChE activity and neuroinflammation as compared to untreated ICV-STZ rats (Table-1). Further, TSA treatment also augments the BDNF levels as compared to untreated ICV-STZ rats (Fig.1b,P<0.05). Based upon these findings, it could be suggested that HDAC inhibition could prove to be beneficial in ICV-STZ induced cognitive deficit and this neuroprotection could be the result of enhanced BDNF based synaptic plasticity as a result of increased histone acetylation.
Reference 1. Paxinos G, Watson C. (1986) (2nd Eds). Academic Press, San Diego.
|