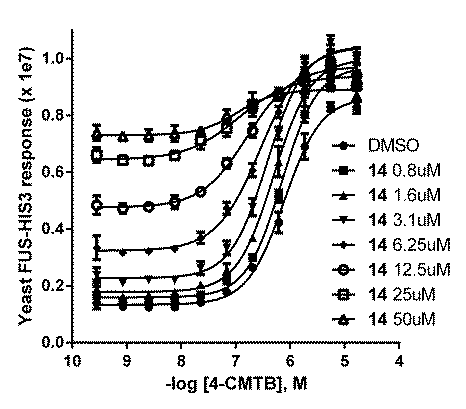
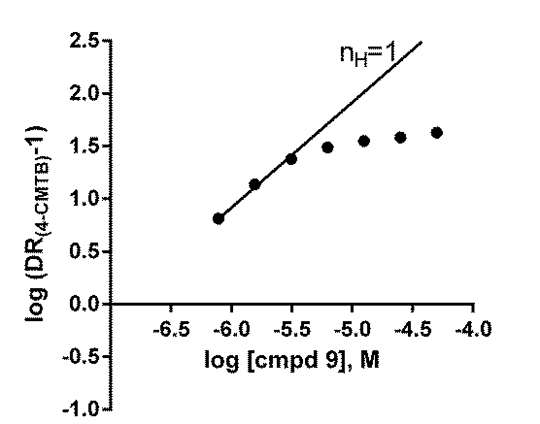
Allosteric and Orthosteric Modulation of the Free Fatty Acid Receptor FFA2 by Bitopic Ligands FFA2 is a G-protein-coupled receptor activated by propionate and other short-chain fatty acids. 4-CMTB is a synthetic agonist selective for FFA2 that lacks a carboxylate group and binds to a site different from propionate, acting allosterically (1). Here, we study bitopic FFA2 ligands containing both carboxylate and N-thiazolylamide, which is the characteristic chemical feature of 4-CMTB. By investigating the allosteric and orthosteric nature of interaction between ligand pairs, we characterise the mode of binding of bitopic ligands to FFA2. [35S]GTPγS-incorporation and yeast reporter assays were used to measure FFA2 activation. Bitopic compounds showed system-dependent efficacy, in contrast to propionate and 4-CMTB (Table 1). Compound 14 ((R)-3-benzyl-4-((4-(2-chlorophenyl)thiazol-2-yl)(methyl)amino)-4-oxobutanoic acid) weakly activated FFA2 in yeast, and showed allosteric cooperativity with 4-CMTB (Fig.1) but not with propionate (not shown). Compound 9 ((S)-4-(4-(2-chlorophenyl)thiazol-2-ylamino)-4-oxo-3-phenylbutanoic acid) acted as an FFA2 inverse agonist in yeast (Table 1). Schild analysis indicated antagonism of propionate by 9 was competitive (n H = 1; pA2 = 6.64±0.17, n=2) but antagonism of 4-CMTB by 9 was allosteric (pKB = 6.88±0.17 and cooperativity factor α= 0.01±0.004 (n=3) using an operational model; Fig.2). Thus, bitopic FFA2 ligands engage the orthosteric site, but appear not to compete at the site of 4-CMTB binding on an FFA2 receptor molecule. It seems paradoxical for two different FFA2 sites to bind the same chemical structure (N-thiazolylamide), and an alternative possibility is that FFA2 has a single N-thiazolylamide site but functions as a homodimer (or higher-order oligomer). This mode of action has recently been proposed to explain allosteric behaviour of a bitopic dopamine D2 antagonist (2), and may be a common mechanism for allosteric interaction between GPCR ligands. Table 1: Activity of FFA2 ligands (pEC50, pIC50 in italic, mean±SD)
Fig.1 Allosterism of 14 and 4-CMTB Fig.2 Allosterism of 9 and 4-CMTB
(1) Lee T et al. (2008) Mol Pharmacol 74:1599-1609. |