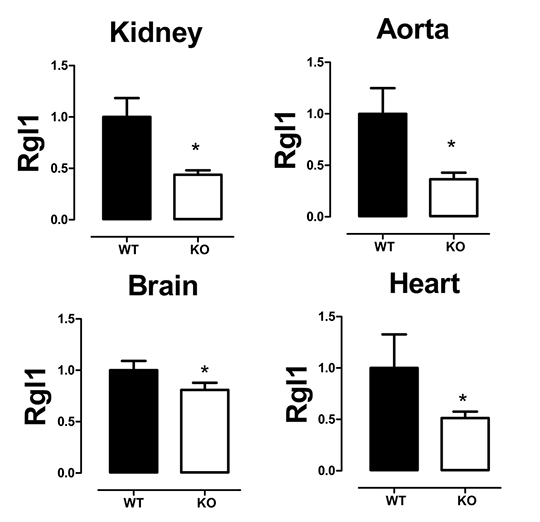
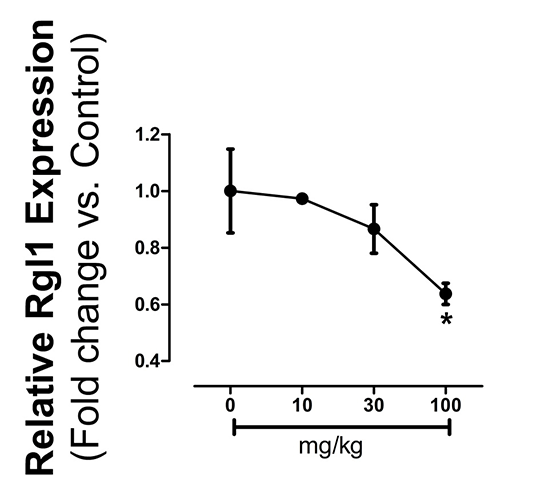
Using Online Microarray Data Mining to Establish the Link Between COX-2 and Rgl1, a Novel Chemopreventative Target for COX-2 Inhibitor Drugs Introduction: Cyclo-oxygenase (COX)-2 is the therapeutic target for non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) including COX-2 selective drugs such as celecoxib (CelebrexTM) and meloxicam (MobicTM). NSAIDs are associated with cardiovascular side effects but have potential in the prevention of cancer. Using a transcriptomic analysis of tissue from atherosclerotic COX-2-deficient mice we have previously identified an interaction between COX-2 and the Ral Guanine Nucleotide Dissociation Stimulator-Like 1 (Rgl1) gene 1. Rgl1 is an effector of Ras, the most common oncogene in human cancer, which activates Ral signaling pathways to regulate proliferation and survival. Down-regulation of Rgl1 may therefore, contribute to the chemopreventative effects of COX-2 inhibitors. Here we have validated our previous studies by performing qPCR analysis of Rgl1 expression on a range of tissues from healthy COX-2-/- mice and mining an online microarray database (Open TG-GATEs) 2 to determine the effect of COX-2 inhibition of Rgl1 expression in a completely independent dataset. Methods: RNA was extracted from kidney, aorta, heart and brain of COX-2-/- mice and wild-type littermates (n=8, male+female, C57Bl/6 background) and Rgl1 expression measured by qPCR relative to 18S and GAPDH housekeeping genes. Publically available microarray data from Open TG-GATEs2 was downloaded (http://toxico.nibio.go.jp/). These were from experiments in which RNA was analysed from liver of rats treated with the COX-2 inhibitor, meloxicam (0-100mg/kg; in 0.5% methylcellulose; by oral gavage; 24hrs). Once downloaded, data were quantile normalised and Rgl1 expression data was produced. Normalised expression at increasing doses was then calculated versus vehicle treated levels.
Figure (A): Expression of Rgl1 in tissues from wildt-ype (WT) and COX-2-/- (KO) mice. n=8. *, p<0.05 by unpaired t-test. Figure (B): Relative expression of Rgl1 in liver of meloxicam-treated rats from Open TG-GATEs. n=3. *p<0.05, by one-way ANOVA. Conclusions: These data validate the link between COX-2 and Rgl1 in two completely independent data sets and demonstrate that Rgl1 down-regulation can be achieved by pharmacological COX-2 inhibition as well as gene disruption. These studies also demonstrate the power and utility of online microarray database mining to generate pharmacological insights. References: (1) Kirkby NS et al. (2014). PLoS One, 9(6): e98165. (2) Uehara T et al. (2010). Mol Nutr Food Res, 54(2): 218-27.
|