Print version
Search Pub Med
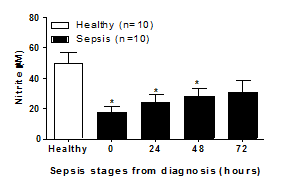
A simple bioassay to detect ‘ iNOS capacity’ of human plasma: Comparison between samples from healthy donors and those with established sepsis. Introduction: Nitric oxide (NO) is formed from L-arginine via the enzyme NO synthase (NOS) of which there are there are three isoforms. Two isoforms are calcium dependent and constitutively expressed in endothelial cells (eNOS) or nerves (nNOS). The third form is calcium independent and induced (iNOS) in various cell types, including macrophages, by pathogens. eNOS and nNOS form relatively low levels of NO whilst iNOS activity is associated with high levels directed at killing pathogens. However, inappropriate or prolonged expression of iNOS is associated with inflammation and septic shock. Amongst other constituents, iNOS activity is affected by exogenous levels of amino acids and associated derivatives. These include the substrate L-arginine, endogenous methylarginine inhibitors (L-NMMA and ADMA), L-citrulline and L-glutamine. In critically ill patients, including those with sepsis, amino acid levels can be compromised and nutritional support may be provided to redress imbalances1. Hypothesis and Aims: In sepsis, investigating the regulation of amino acids and methylarginine, related to iNOS activity, will deepen our understanding of disease progression. Moreover, the net result of changes in inflammatory mediators may lead to future biomarkers. However, the consequences of amino acid (and other) changes in plasma from septic patients for iNOS activity cannot be estimated by simply measuring levels of amino acids and/or NO. Therefore, a key aim was to develop a simple ‘bioassay’ using LPS activated murine macrophages to test the net effects of sepsis on the ability of human plasma to support iNOS activity ex vivo. Methods and Results: RAW murine macrophages were cultured in 96-well plates, stimulated with LPS (1μg/ml) for 24 hours and nitrite measured as an indicator of NO formation using the Griess assay as described previously2. In pilot studies using plasma from healthy volunteers, LPS induced iNOS activity (μM) in RAW cells (basal, 0.6±0.14; LPS, 47.4±4.8; n=6 wells, plasma from 2 separate donors). Plasma sample collection was performed after ethical review by Royal Brompton, NHS trust (code:01-152). In the main study, we compared directly the iNOS activity in LPS treated RAW macrophages incubated in the presence of 100% plasma from 10 healthy control donors and 10 patients with sepsis at diagnosis, after 24-72 hours. The level of iNOS activity detected in RAW cells was reduced significantly by septic plasma at 0 hours; 17.59 ± 6.981, p=0.0011 , 24 hours; 24.21 ± 4.842,p=0.0108 and 48 hours; 27.96 ± 5.481, p=0.0347) compared to healthy controls (control; 50.23 ± 6.981) (Figure 1).
Figure 1: iNOS activity in LPS (1μ g/ml) treated RAW macrophages incubated in the presence of 100% plasma from healthy volunteers (open column) or patients with sepsis at diagnosis and after 24-72h (closed column). Data is the mean ± SEM for n=10 (sepsis) and n=10 (healthy). *p<0.05, one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett's post-test. Discussion: The capacity of plasma from septic patients to ‘support’ iNOS activity is reduced, which may reflect changes in relevant amino acids and methylarginines. The usefulness of this assay in predicting clinical outcomes and/or guiding nutritional supplementation remains the subject of investigation. (1) Hayes, G. L. et al. Adv Crit Care 22, 301-316; (2011). (2) Swierkosz, T. A. et al. Br J Pharmacol 114, 1335-1342 (1995). (3) Swierkosz, T. A., Mitchell, J. A., Warner, T. D., Botting, R. M. & Vane, J. R. Co-induction of nitric oxide synthase and cyclo-oxygenase: interactions between nitric oxide and prostanoids. Br J Pharmacol 114, 1335-1342 (1995).
|