Print version
Search Pub Med
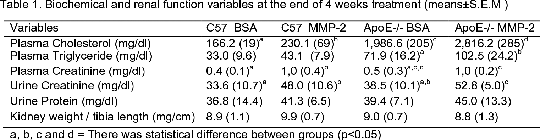
RECOMBINANT HUMAN MMP-2 INCREASES KIDNEY DISEASE IN ATHEROSCLEROTIC MICE. Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) are key enzymes in the degradation of extracellular matrix (ECM) that keeps in balance structural and functional integrity of various tissues (1). However, the imbalance promoted by some diseases can cause serious damage to major organs (1,2). It is known that changes in the expression or activity of MMP-2 is related to heart and kidney disease (2,3). Therefore, this study aimed to investigate whether higher levels of circulating MMP-2 could lead to future progression of renal disease in atherosclerotic mice. Recombinant human MMP-2 (rh-MMP-2) was expressed and purified from E. coli. Daily 1.2 µg/ml of MMP-2 or Bovine Serum Albumin (BSA) was injected in health (C57) and atherosclerotic mice (ApoE-/-) for 4 weeks. All animals were fed a high-cholesterol diet (1.5%) for 7 weeks. Kidneys (n = 20) were collected and frozen in OCT to verify the activity of MMP-2 with in situ zymography using DQ-Gelatin. Plasma (n = 8) was collated and cholesterol, triglyceride and creatinine concentrations were determined by an enzymatic assay. To determine the protein and creatinine concentration in urine were collected using a metabolic cage. The animals were grouped into pools (samples were pooled from five mice). To verify the localization of MMP-2 in vivo, the catalytic domain of the human MMP-2 was cloned and fused with the green fluorescent protein (GFP). The clone was expressed and purified from E coli. MMP-2-GFP (1.2 µg/mL) was injected in health (C57) and atherosclerotic mice (ApoE-/-) for 4 weeks. The MMP-2-GFP was tracking using IVIS-Spectrum for GFP. Data represent mean ± S.E.M and the results were statistically analyzed using one-way ANOVA with Tukey pos-hoc test (p<0.05). Kidney treated with MMP-2-GFP showed a higher concentration compared with the control. The same way, in situ gelatinolytic activity in the kidney was increased in animals exposed to MMP-2/ApoE (13,0± 1,6 , n = 5) and MMP-2/C57 (12,7± 1,7, n = 5) compared to vehicle BSA/ApoE (11,6± 1,2, n = 5) and BSA/C57 (9,3± 1,0, n = 5). Biochemical tests showed blood and urinary alterations in rats treated with MMP-2 (table 1).
The results suggest the spread of MMP-2 via the circulation to the kidneys induces funtional and structural damage. (1)Schiffrin EL et al. (2007). Circulation 116: 85-97 (2)Dimas GG et al. (2013). Hippokratia 17(4):292-297 (3)Xu T et al. (2014). Renal failure 36(5): 666-672
|