Hemin blunts the depressant effect of chronic nicotine on reflex tachycardia in female rats via activation of central NOS/PI3K pathway
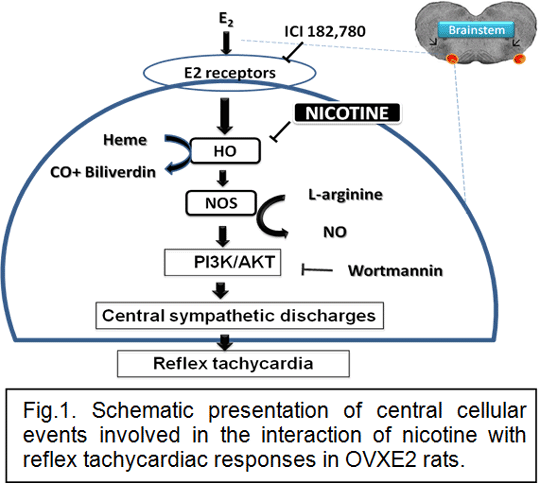
Our previous reports showed that chronic nicotine impairs reflex heart rate responses to arterial baroreceptor unloading in female Wistar rats (1). As the nicotine effect disappears in ovariectomized (OVX) rats and restored after estrogen (E2) replacement, it is concluded that the nicotine-baroreflex interaction is E2 dependent. In this study, we investigated whether the products of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) and/or heme oxygenase (HO) and their downstream soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC)/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) signaling mediate the E2-dependent baroreflex depressant effect of nicotine in conscious rats. Baroreflex curves relating reflex tachycardic responses to falls in blood pressure generated by sodium nitroprusside were established and slopes of the curves served as a measure of baroreflex sensitivity (BRS). Values are expressed as means ± S.E.M (n = 6-8) and analysis was performed using one way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by the Tukey’s post-hoc test. Compared with saline values, nicotine (2 mg/kg/day i.p. for 14 consecutive days) significantly reduced BRS in OVXE2 (-1.8±0.1 vs. -1.1±0.2 beats/min/mmHg) but not OVX rats (-2.1±0.2 vs. -2.2±0.3 beats/min/mmHg). The BRS depressant effect of nicotine in OVXE2 rats disappeared after treatment with hemin (HO inducer) but not L-arginine (NOS substrate) denoting the importance of reduced availability of CO, but not NO, in the nicotine effect. The favorable BRS effect of hemin was abolished after central pharmacologic inhibition of NOS (L-NAME) or PI3K (wortmannin) in central neurons, highlighting the importance of NOS and PI3K as downstream effectors of HO. We also report that central neuronal circuits of MAPKs do not appear to be required for the elicitation of the baroreflex facilitatory effect of hemin because the latter was maintained after central inhibition of MAPKERK (PD98059), MAPKp38 (SB203580) or MAPKJNK (SP600125). Also, guanylyl cyclase inhibition (ODQ) or E2 receptor blockade (ICI 182,780) failed to alter the BRS effect of hemin.
It is concluded that hemin improves the E2-specific depressant effect of nicotine on reflex tachycardia through downstream activation of central NOS/PI3K signaling (Fig. 1). (1) El-Mas MM et al. (2012). J Pharmacol Exp Ther 342:568-575.
|