Print version
Search Pub Med
Synergistic inhibition of NADPH oxidase inhibitors and gp91-phox specific inhibitor, gp91ds-tat, with clopidogrel on ADP-induced human platelet activation and aggregation
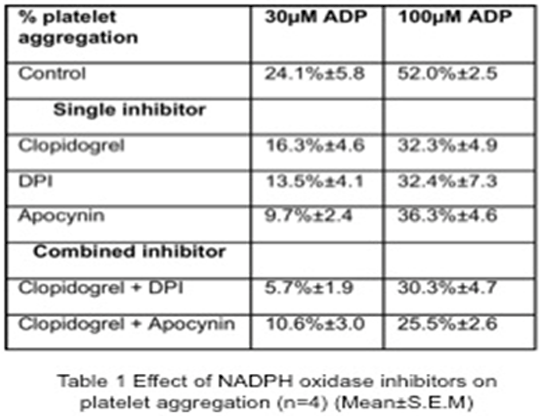
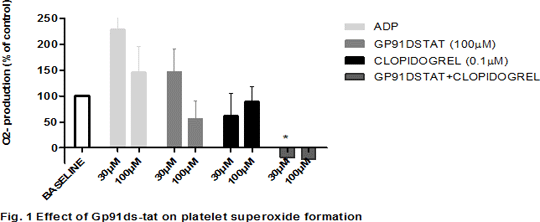
Platelet activation plays an important role in vascular homeostasis and in the onset of thrombotic complications. NADPH oxidase (NOX) is one of the most important enzymatic systems involved in reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation. Platelet NOX consists of 3 cytosolic subunits and 2 membrane-bound; gp91-phox and p22-phox (1). The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of NOX inhibitors, apocynin and diphenyliodonium (DPI), as well as gp91ds-tat, a specific gp91-phox inhibitor on ADP-stimulated platelet function. Human platelet-rich plasma (PRP) was preincubated with, apocynin (50µM), DPI (50µM), and gp91-dstat (100 µM), either alone or in combination for 30 minutes at 37OC before addition into a 96-well plate in the presence of ADP (1- 300 µM).Platelet aggregation and adhesion were performed according to previous methods (2). Platelet activation was measured by measuring the expression of PAC-1 binding and P-selectin using flow cytometry. Washed platelets were used in the determination of ROS according to published chemiluminescence assay (3). In addition to this, study of combination of NOX inhibitors and clopidogrel (0.1µM) were also performed. Data are given as mean±SEM and analysis was performed using One-way ANOVA using GraphPad Prism 6.0. In NOX inhibitor-treated PRP, ADP-induced platelet aggregation was reduced (Table 1). Combination of NOX inhibitors and clopidogrel produced synergistic inhibition of aggregation. Similar observations were made in platelet adhesion, and in gp91d-stat–treated PRP. Both NOX inhibitors and gp91ds-tat reduced platelet activation marker expression in late platelet activation (data not shown) and platelet superoxide production (Fig 1.)
In summary, combinations of clopidogrel and either NOX inhibitors or gp91ds-tat synergistically inhibit platelet function stimulated by ADP. The inhibitory effects of gp91ds-tat on platelet activation and ROS formation confirm the involvement of platelet NOX in ADP activation pathways. Thus, platelet NOX pathway is important in ADP-induced platelet aggregation, adhesion and expression of platelet activation markers through generation of superoxide. References: 1) Violi F et al. (2014). Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 111: 817-823. 2) Armstrong PCJ et al. (2008). Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 6: 1933-1943. 3) Krotz et al. (2002). Blood, 100(3): 917-24.
|